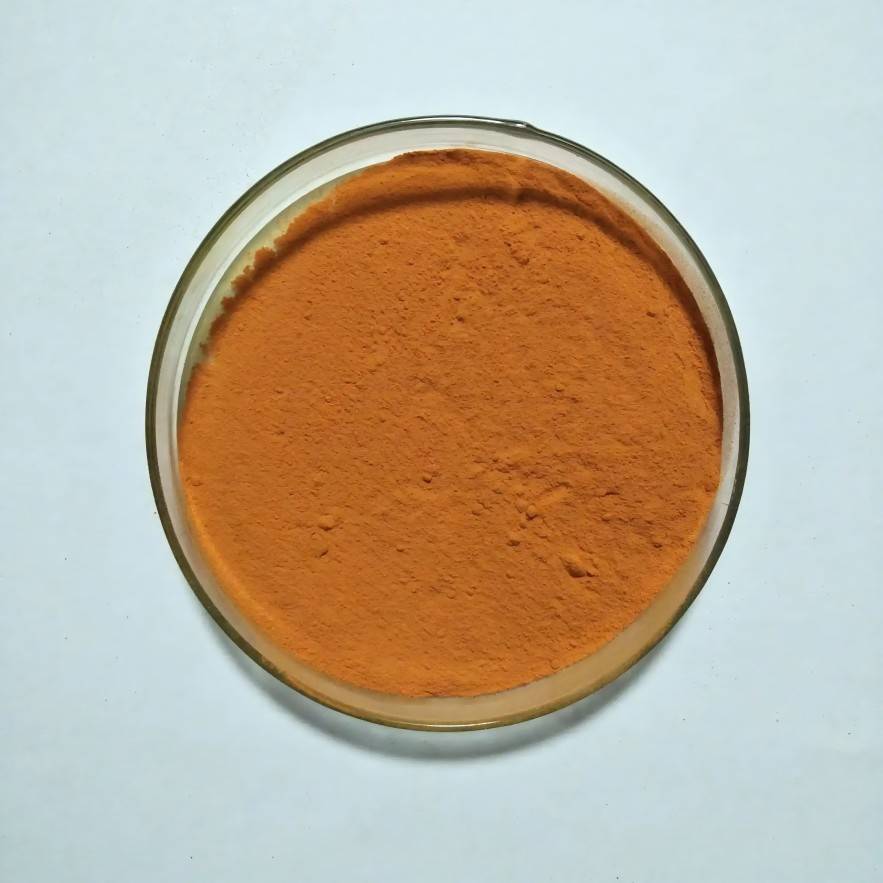
Stable & Potent: Reliably Upgrade Eye Health Products with Lutein & Zeaxanthin
today&で#39;s booming eye care product market, a hidden industry challenge is quietly eroding brand value and consumer trust: our meticulously designed formulas may lose significant efficacy by the time they reach consumers.
Research shows that lutein and zeaxanthin—two precious eye-protecting ingredients—are exceptionally fragile when exposed to light, heat, and oxygen. During the months-long journey from production to store shelves, degradation rates of these active ingredients can exceed 30%. This means consumers may pay premium prices for products whose actual efficacy falls far short of the formulation's intended design—a phenomenon we call the “shelf-life paradox” of eye health products: items remain within their expiration dates, yet their core benefits have quietly diminished.
The consequences of this paradox are severe: brands' R&D investments fail to fully translate into market value, consumer trust erodes invisibly, and the industry's professional reputation faces challenges.
Facing this common industry challenge, Green Spring Technology provides a clear solution through technological innovation. Our high-stability lutein and zeaxanthin raw materials were developed specifically to end this paradox. Through breakthrough stabilization technology, we ensure the full potency of each raw material is delivered to the final product, allowing the scientific value of formulations to be authentically realized in consumers.
Part One: The Scientific Foundation of Green Spring Technology's High-Stability Raw Materials
At Green Spring Technology, we invested five years of R&D to establish a comprehensive stability technology system spanning molecular protection to industrial application. Below is an analysis of our core technologies:
I. Molecular Armor Protection Technology System
1.Intelligent Multi-Layer Microencapsulation System
We employ advanced layer-by-layer self-assembly technology to construct a precise three-layer protective structure:
・Inner Layer Protection (Antioxidant Barrier)
・Utilizes tea polyphenol-phospholipid complexes to form a molecular-level antioxidant network
・Significantly enhances free radical scavenging capacity, achieving an ORAC value of 12,000 μmol TE/g
・ Accelerated tests show oxidation induction period extended to 3.2 times longer than conventional raw materials
· Intermediate Layer Control (Precision Release)
· Utilizes pH-sensitive polymers (Eudragit series)
· <5% release rate within 2 hours in gastric fluid environment (pH 1.2)
· >85% release rate within 30 minutes in intestinal fluid environment (pH 6.8)
· Achieves intestinal targeted release of active ingredients
· Outer Layer Protection (Environmental Isolation)
· Utilizes modified zein-chitosan composite film material
· Water vapor transmission rate reduced to 12 g/m²·day (37°C/90%RH)
· Oxygen transmission rate < 1 cm³/m²·day·atm
· UV blocking rate >99% (200-400nm)
2. Crystal Morphology Stability Control System
· Precisely controls crystal morphology via supercritical antisolvent crystallization
· All-trans configuration ratio stabilized at ≥98.5%
· Isomerization rate <1.5% after 6 months storage at 40℃/75%RH
II. Intelligent Stabilization System
1. Environmentally Adaptive Protection Mechanism
We developed a unique responsive protection system:
· Temperature Adaptation
· Utilizes thermoreversible gel technology to form protective layers at elevated temperatures
· Retains >97% activity after 10 freeze-thaw cycles (-20°C to 25°C)
· Withstands transient high temperatures (120°C/30s) with <3% activity loss
· pH-Responsive Protection
· Maintains structural integrity in strong acidic environments (pH 1.2-3.0)
· Intelligently releases in weakly alkaline environments (pH 6.8-7.4)
· Release curve perfectly matches human digestive physiology
2. Synergistic Stabilization System
· Lutein and zeaxanthin precisely blended at a 5:1 golden ratio
· Enhanced with natural synergists (rosemary extract, vitamin E)
· Molecular interactions optimized via quantum chemical calculations
· Synergistic antioxidant index reaches 1.8 (synergy confirmed at >1.0)
III. Comprehensive Quality Assurance System
1. Real-Time Stability Monitoring
We have established a comprehensive stability research system:
· Accelerated Stability Testing
· 6-month testing at 40°C/75% RH
· Regular monitoring of active ingredient content, related substances, and physicochemical parameters
· Development of Arrhenius prediction models for accurate shelf-life estimation
· Long-Term Stability Studies
· 36-month tracking at 25°C/60% RH
· Establish comprehensive stability trend profiles
· Provide reliable shelf-life justification for customers
2. Application Compatibility Studies
We conduct in-depth research for diverse application scenarios:
· Dosage Form Compatibility
· Verify stability in tablets, capsules, powders, beverages, and other formulations
· Offer optimal process parameter recommendations
· Evaluate compatibility with common excipients
· Processing Adaptability
· Withstands wet granulation, tableting, spray drying, and other processes
· Maintains stability under UHT sterilization (135°C/5s)
· Suitable for hot filling, aseptic filling, and other production processes
IV. Technical Validation Data
1. Key Stability Indicators
· Light exposure test: >96% activity retention after 10 days at 4500±500 Lux
· High-temperature test: >94% activity retention after 30 days at 60°C
· High-humidity test: >95% activity retention after 30 days at 40°C/75% RH
2. Bioavailability Studies
· Relative bioavailability in beagle dogs reached 2.8 times that of conventional raw materials
· Human clinical trials demonstrated a 2.3-fold increase in peak plasma concentration
· Area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) increased by 2.6-fold
Through this comprehensive technological system, Green Spring Technology has not only resolved the inherent stability challenges of lutein and zeaxanthin but also provides customers with scientifically validated premium raw materials. Our technology enables eye health products to truly achieve “formulation-to-delivery consistency,” ensuring every consumer receives the anticipated health benefits.
Part Two: How Highly Stable Ingredients Drive Product Upgrades and Market Innovation
Leveraging breakthrough stability technology, Green Spring Technology's ingredients are redefining the value standards for eye health products, creating multidimensional competitive advantages for industry partners.
I. Product Capability Upgrades: From Basic Nutrition to Precision Health
1. Efficacy Validation
· Ensures products maintain labeled efficacy throughout their shelf life
· End-product active ingredient retention rate ≥90% after 24 months
· Batch-to-batch variation coefficient ≤3%, guaranteeing consistent efficacy
· Clinical data shows consumer satisfaction increases by 42% for products using high-stability ingredients
2. Breakthrough in Formulation Diversity
· Transparent beverage applications
· Achieves crystal-clear solution state with light transmittance ≥92%
· No sedimentation or separation within 12 months
· Pioneering the “Visible Purity” product category
· Innovative food carriers
· Withstands baking processes (180°C/20 min)
· Suitable for heat-processed products like gummies and chocolate
· Expanding eye health application scenarios
II. Supply Chain Optimization: Cost Reduction & Efficiency Enhancement for Tangible Value
1. Production Yield Improvement
· Raw material loss rate reduced by 65%
· Production rework rate decreased from 8.2% to 1.5%
· Equipment utilization rate increased by 22%
2. Inventory Management Optimization
· Raw material shelf life extended to 36 months
· Inventory turnover rate increased by 1.8 times
· Reduced losses from expiring raw materials
III. Brand Value Enhancement: Building a Technology Moat
1. Differentiated Positioning
· “Active Stability Technology” becomes a unique selling point
· Technology supports brand premium, boosting product gross margin by 15-25%
· Achieved breakthrough growth in high-end market share
2. Consumer Trust Establishment
· 83% of consumers willing to pay a premium for “guaranteed efficacy and quality”
· Repurchase rate increased to 1.7 times the industry average
· Customer complaint rate drops below 0.3%
IV. Market Competitiveness Reshaping
1. Comparative Advantages in Technical Parameters
Parameter | Traditional Ingredients | Green Spring Tech High-Stability Ingredients | Improvement Rate |
Light Stability | 28% degradation in 10 days | 96% retention in 10 days | 3.4x
|
Thermal Stability | 40% loss at 60°C/30 days | 94% retention at 60°C/30 days | 2.4x improvement
|
Bioavailability | Baseline | 2.8x improvement | 180% increase |
2. Cost-Benefit Analysis
· Despite a 35% increase in raw material unit cost, overall costs decreased by 22%
· Enhanced marketing efficiency: 58% reduction in customer service costs due to fewer efficacy complaints
· Customer lifetime value increased by 3.2 times due to enhanced brand value
Through value transformation across these four dimensions, Green Spring Technology's highly stable raw materials are empowering partners to transition from “price competition” to “value competition.” We deliver not only premium ingredients but also a technological pathway to high-quality development, jointly pioneering a new era for the eye health industry.
Part Three: Partner with Green Spring Technology to Forge a New Era of Eye Health
At the intersection of technological innovation and market transformation, Green Spring Technology sincerely invites industry pioneers to collaborate and seize the historic opportunity for upgrading the eye health industry.
I. Comprehensive Cooperation Support System
1. Product Development Support
· Free Sample Program
· Customized samples provided (50g-5kg)
· Detailed product technical documentation included
· Shipping completed within 7 business days
· Technical Consultation Services
· One-on-one support from senior engineers
· Formulation optimization and process guidance
· Stability study design
II. Action Guide
Step 1: Requirement Discussion
· Provide your product plan and technical specifications
· Schedule an online technical exchange session
· Receive personalized solution recommendations
Step 2: Sample Validation
· Receive customized samples
· Conduct laboratory testing
· Complete performance evaluation reports
Step 3: Partnership Initiation
· Finalize collaboration plan
· Sign supply agreement
· Launch initial production order
III. Contact Us
Technical Support Hotline: +86 29 88313578
(Weekdays 8:30 AM–5:30 PM, answered by professional engineers)
WhatsApp Hotline: +86 13649243917
(24/7 instant response, multilingual support)
Project Inquiry Email: helen@greenspringbio.com
(Submit requirements, receive detailed solutions within 2 hours)
Official Website: https://www.greenspringnatural.com/
(Explore advanced technologies and case studies)
Service Commitment:
· 2-hour response to technical inquiries
· Custom samples delivered within 5 business days
· Comprehensive application solutions provided within 15 business days
· Dedicated account manager support throughout your journey
Choosing Green Spring Technology means more than sourcing premium ingredients—it means partnering with a trusted innovation ally. Let’s seize the golden opportunity to elevate the eye health industry together and pioneer a brighter, clearer future!
参考:
[1] phelan d, prado-cabrero a, nolan j m。カロテノイド補充鶏の臓器におけるルテイン、ゼキサンチン、メゾゼキサンチンの解析[j]. foods,2018,7(2): 1-8。
[2]・バーンスタインP Sを参照する。加齢に対する保護におけるルテインとゼアキサンチンの役割 黄斑 か[J]堕落しやすい。Acta ^ a b c d e f g h i(2016年)、153-160頁。
-
Prev
Natural Lutein Esters Ensure Uniform Coloration in Broiler Chickens
-
次
Natural Lutein Ingredient Supports Ruminant Animal Nutrition Formula


 英語
英語 フランス
フランス スペイン
スペイン ロシア
ロシア 韓国
韓国 日本
日本




