医学植物羅漢国の研究
Siraitia grosvenorii (Swingle) C. Jef-frey ex Lu et Z. Y. Zhang is the dried fruit of a dioecious, dioecious perennial vine in the family Cucurbitaceae. It is cool in nature, sweet in taste, and enters the lung meridian. It has the effects of clearing away heat from the lungs, moistening the lungs, relieving sore throat and improving voice, and lubricating the intestines to promote bowel movement. It is used to treat cough due to lung heat, sore throat with loss of voice, and constipation due to dryness in the intestines [1]. As a precious medicinal and sweetening plant unique to China, Luo Han Guo is mainly produced in Yongfu, Lingui and Longsheng, etc., in Guangxi. The fruit of Luo Han Guo contains a variety of sweet glycosides, among which Mogroside V is one of the strongest non-sugar sweeteners in the world, about 300 times sweeter than sucrose. It is widely used in foods, health products and medicines, and is an ideal sugar substitute for diabetics, obese people and hypertensive patients [2]. This paper reviews the taxonomic status, geographical distribution, main cultivated varieties, breeding and cultivation techniques, chemical composition, pharmacological effects and molecular biology research of Luo Han Guo, with a view to providing a reference for further in-depth research, development and utilization of Luo Han Guo.

シロイヌナズナ科シロイヌナズナ属の1種
siraitia grosvenoriの分類学に関して、メリルは1934年にs . silomaradjaeを模式種として新属siraitiaを設立したが、正式には認められなかった。羅漢國は1941年、アメリカスウィングル社が広西永福県で採集した標本tan yinghua no . 1を基に同定し、ウリ科momordica属に分類した。1979年、この標本を受講し、英国の植物学者ジェフリー・ハン被告属さない直轄郭と結論づけThladiantha属のがMomordica属の触手事実に基づいて先端は3分(だけ増分工場では、ケーブル、ツイスト上下の分岐点と罗汉果物には属さない属MomordicaでもThladiantha属にはと命名Thladiantha grosvenorii (Swingle)・c・ジェフリー。この点に関して、中国の多くの学者は懐疑的である[3]。1997年、zhuang weijianらは、羅漢国の染色体数がx = 14であること、tribulus属の染色体数がx = 9であること、momordica属の染色体数がx = 11または14であることを最終的に決定した。また、羅漢国の花粉の形態は、花粉の大きさと網目の大きさを除けば、ヒエラルキーやヒエラルキーの花粉とは大きく異なり、より似ている[5]。
1980年、ジェフリーズに移籍#中国科学院植物研究所のlu anminらは標本を調査するために中国を訪れ[6]、ローハンの果実群の雄の葯が突出しているか、または湾曲しており、種子が著しく大きく、momordica属とは明らかに異なっていると結論付けた。また、雌花と雄花には苞がないこと、雄蕊が3本ではなく5本であること、果実の皮が滑らかで塊状の突起がないことから、momordica属に分類できないと結論付けました。そのため、シライティアを分離して新属を設立することが提案された。その後、ジェフリーはmerrillが論文" east asian cucurbitaceae "で提唱したsiraitiaという属名を使用し、siraitiaのすべての種をsiraitia属に移した。現在、植物分類学を受けさせジェフリーのが手間取り主張で、Luリュ・ヒソンらは[6]1984年、の学名Siraitia grosvenorii (Swingle)・c・ジェフリー・張exネルたちz yはSiraitia grosvenorii (Swingle)・c・ジェフリー・張exネルたちz yとにはSiraitia属の植物家庭でCucurbitaceaeます。しかし、初期の文献では、siraitia grosvenoriiはthladi-anthaやmomordica grosvenoriiと書かれることもある。
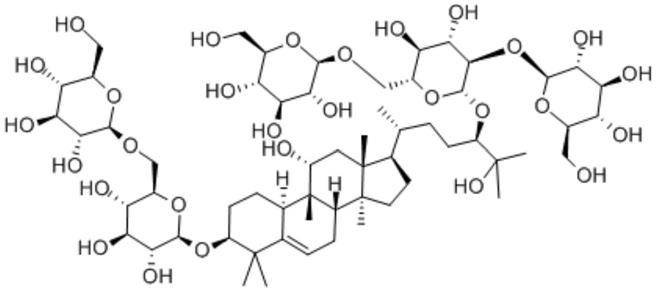
2. 学名はsiraitia grosvenorii
主に中国の広西、広東、湖南、貴州、海南、江西省の一部の山岳地帯に分布しています。これらの地域は湿度の高い熱帯・亜熱帯気候であり、標高は250 - 1,400 m、東経106.5 - 115.0度、北緯21.0 - 24.5度である。 しかし、分布は均一ではない。その中でも広西の永福県と臨沂県は羅漢国の栽培の中心地である[7]。羅漢国は広西チワン族自治区に広く分布しており、東は賀州市の肇平県、南は欽州市の浦北県、西は百色市の凌雲県、北は桂林市のlingui県などがある。このうち、金秀ヤオ族自治県の大鹿山が最も集中して分布している[8]。
luohanguoの3つの主要な栽培品種
羅漢国の主な栽培品種は、青豚国、東莞国、荒建国、長灘国、洪茂国、茶三国である。厳重な危害ウイルス病によるによりroot-knot線病気細菌約束ショウジョウバエなど組織培養の使用は苗伝搬の目的を達成できる快速の優良品種の伝搬・浄化とそのため、ここ数年来、培養組織の若苗ボーリングなどの小輪種やQingpi物など手がけるなど幅広く、ハン被告郭产地のように進められる。このうち、3号は2号の緑色の果皮から選抜に成功した羅漢果の新品種だ。先端の芽の消毒と急速な増殖、方向栽培と浄化と若返りを経て、2003年に栽培に成功した。
It has excellent characteristics such as wide adaptability, well-developed roots, vigorous growth, drought and fertilizer tolerance, concentrated flowering, early fruiting and high yield, low pest and disease damage, few physiological fruit cracks, high rate of medium and large fruits, good quality, and stable seed characteristics [9]. Yongqing No. 1 is a female clonal variety that was produced by crossing a winter melon fruit as the male parent with a Longjiang green-skinned fruit as the female parent, followed by two years of single plant selection and tissue culture breeding. The fruits of this variety are long and oval, with a large fruit rate of up to 73.48% with an average single fruit weight of 100 g. The content of sweetener V, total fruit glycoside, total sugar, water extract and vitamin C is as high as 1.03%, 8.84%, 17.40%, 37.90% and 3.02 mg/g, respectively. It has good yield and strong stress resistance, with up to
1ヘクタール当たり165,000[10]。
4羅漢国の布教と栽培技術
羅漢国の主な伝統的な繁殖技術は、種子の繁殖、塊茎の繁殖、層化の繁殖、挿し木の繁殖、接ぎ木の繁殖である。の厳しい状况にあり、ウイルスの病気root-knot線の病気やハエinfestations、産地として悪影響が伝統的な植えパターンの森林破壊などの山林の負担を増やす環境土壌浸食し、棲息地の劣化など一方、伝統伝搬技術が次々に変化しましたまた、組織培養を用いてウイルスフリーの苗を得る実験研究も大きく進展している[11,12]。このうち、広西汉方薬の植物園、植物広西院に金桂林のレベルが高くて新しい区ベルリンバイオテクノロジー有限公司は、限公司は選択年に従事してきた繁殖し、急速に伝搬優秀な菌株Luohanguo近年、ストレスは多少改善されたある程度Luohanguoの抵抗を達成し、民主化を成し遂げた増産と品質を上げることでした現在、青皮、博林などの品種の組織培養苗は、生産地域で広く普及している;一方で、伝統的な洛漢国の丘陵栽培法を平地栽培法に転換しようとする試みも多く行われている[13]。
5 luohanguoの化学組成
5.1ククルビタントリテルペノイドとその配糖体
At present, the main triterpenoid and its glycosides isolated and identified from the fruit of Luohanguo are: Simonoside I, Mogroside II E, Mogroside III, Mogroside III E, Mogroside IV, Mogroside V, 11-oxo-Mogroside V [14], Mogroside ⅣA and Mogroside ⅡA1 [15], Luohanguo digolyl benzoate [16], and Luohanguo neoglycoside [17]. The above components are the main sweet components of Luohanguo, accounting for 3.755% to 3.858% of the dried fruit content. Among them, Mogroside V is the main sweetening component, while Simonoside I is the sweetest component of the cucurbitane triterpene glycosides. When its content is 0.01%, the sweetness of the two is 256 to 344 times and 563 times that of a 5% sucrose aqueous solution, respectively. In addition, Luo Han Guo acid A and Luo Han Guo acid B [18] and Luo Han Guo acid E [19] have been isolated and identified from the root of Luo Han Guo.
5.2タンパク質とアミノ酸
徐偉坤(xu weikun)ら[20]は、乾燥させた羅漢果のタンパク質含有量が7.1% ~ 7.8%であることを発見した。加水分解物には、検出されなかったトリプトファンを除いて、人体に必要な8種類のアミノ酸を含む18種類のアミノ酸が含まれています。最も多く含まれているのはグルタミン酸とアスパラギン酸で、羅漢国には一定の栄養価があることを示しています。
5.3フラボノイド
Si Jianyong et al. [21] isolated two flavonoid glycoside components from fresh Luo Han Guo aqueous extract: kaempferol-3,7-α-L-dirhamnoside and kaempferol-3-O-α-L-rhamnoside-7-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-2)-O-L-rhamnoside]. Chen Quanbin et al. [22] isolated and identified kaempferol-3,7-O-α-L-dirhamnoside and quercetin-3-O-β-D-glucose-7-O-α-L-rhamnoside from the leaves of Luo Han Guo, with kaempferol and quercetin as the aglycones. Liao Riquan et al. [23] isolated and identified luohangol benzoate, bis[5-formylfurfuryl] ether, 5-hydroxymethyl furfuroic acid, succinic acid, magnolol, kaempferol, kaempferol-3,7-0-a-L-dirhamnoside, of which bis[5-formylfurfuryl] ether, 5-hydroxymethyl furfural and magnolol were isolated from Luo Han Guo for the first time.
5.4他の成分
The fresh fruit of Luo Han Guo contains D-mannitol[24];熟れた果実は26の無機質元素(人体に必要な16の元素)を含み[25]、多量のブドウ糖と果糖を含む[26];種子油は不飽和脂肪酸が豊富です[27]。
6羅漢郭の薬理作用
6.1去痰薬と咳抑制剤の効果
Luo Han Guo Mogroside V can increase the secretion of phenol red in the trachea of mice, promote the movement of mucus in the esophagus of frogs, and inhibit ammonia-induced coughing in mice. However, it has no significant effect on guinea pig asthma induced by citric acid, indicating that Luo Han Guo sweet glycosides have expectorant and antitussive effects [28].
6.2抗菌作用がある
su huanqunら。[29]その濁度によって発見されました羅漢国文書can significantly limit the growth and acid production ability of Streptococcus mutans, thereby inhibiting its cariogenic effect. The inhibition rates of the ethanol extract of the leaves and stems of Luo Han Guo (50.0 mg/mL) on Pseudomonas aeruginosa were 90.9% and 76.7%, respectively. In addition, the inhibition rate of the above stem extract on Escherichia coli was also as high as 70.2% [30].
6.3免疫機能
羅漢国糖配糖体は正常なマウスの免疫機能には有意な影響を与えないが、マクロファージの貪食機能とシクロホスファミド(ctx)免疫抑制マウスのt細胞の増殖効果を有意に改善することができる[31]。羅漢国の水抽出物は、正常なラットの体液性および細胞性免疫機能を高め、マウスの非特異的免疫機能を改善することができる[29]。
6.4抗がん効果
luo han guo抽出物を用いたマウスのin vitro試験では、luo han guo sweetin vの抗がん効果がステビオシドと同等かそれ以上であることが明らかになった[32]。
6.5抗酸化作用
Monk fruit extract can effectively remove free radicals, inhibit the oxidation and hemolysis of red blood cells, and the production of malondialdehyde (MDA), indicating that it has antioxidant activity, and monk fruit glycosides are the main antioxidant active ingredients [33].
7 .モンクフルーツの分子生物学研究
分子生物学研究初期ハン被告郭氏はなど分子マーカー技術を利用した研究に限られていたRFLP (34) RAPD(ソ・ジャンフン)ISSR (38) AFLP (39) SRAP(40)を確認して勉強し種の遺伝的多様性は高くなりされた親類書にセックス識別遺伝子背景指紋と遺伝子ハン被告郭の地図で作り出されたものです研究者二代目高速スループットSolexa配列技術を行う高スループットのソートLuohanguoの果実のtranscriptome表現プロファイル3 d受粉は後50 d 70 d 43,891取得Unigenes、うち、739関連代謝をLuohanguo二次60 Unigenesテルペン骨格合成に熱中している。トランスクリプトームのデータを用いて、羅漢国糖鎖vの生合成経路に含まれる20の羅漢国糖鎖骨格合成遺伝子と2種類の構造修飾遺伝子(シトクロムp450遺伝子と糖転移酵素遺伝子)の全遺伝子が発見された。また、80のp450遺伝子、72の糖転移酵素遺伝子、90の糖転移酵素遺伝子が得られた。発現プロファイルのスクリーニングと組み合わせることで、ロガニンvの合成に関連する可能性のある6つのudpg候補遺伝子が得られた。race技術を用いて、全長の16個の骨格合成遺伝子と5 'または3 '断片をもつ2個の遺伝子、全長の6個のcyp450遺伝子、全長の7個のグルコシルトランスフェラーゼ遺伝子がクローニングされた。今回のトランスクリプトームと発現プロファイルの解読は、羅漢国の機能ゲノムと甘味料の生合成の分子機構の研究に強固な基盤を与えるものである。
8展望
羅漢果は漢方薬と食用植物の重要な資源として、中国の有名な特産品であり、伝統的な輸出商品である。しかし、ウイルス病、根knot線虫病、ショウジョウバエは、羅漢国産業の健全な発展を妨げてきた。したがって、栽培環境、植物、果物の汚染の農薬汚染を避けるために、化学薬品の使用を最小限に抑えるために、農業と生物学的なコントロールを中心とした総合的なコントロール方法を実施する必要があります;病気や虫に強い羅漢国品種の育成にも努力しなければならない。

羅漢国は、植栽環境、狭い植栽面積、再植栽の障壁に厳しい要件を持っています。連続作付の作物は害虫や病気に非常に弱く、毎年作付面積を変えるには多くの人手、物的資源、資金が必要です。また、現在の生産地では伝統的な栽培方法が主流で、山林の伐採が多く、土壌の浸食や生息地の劣化などの悪影響をもたらしています。著者はこのような理由から、羅漢国の連続耕作の障害を一日も早く克服するために、田植え現場の土壌微生物に対する研究を強化しなければならないと考えている。
Luo Han Guo is a unisexual, dioecious plant. The pollen of male flowers is heavy and sticky, and has a bitter taste. Relying solely on wind or insects to spread pollen will not result in a high rate of fertilization. Only artificial pollination can ensure production, and pollination is the process that requires the most labor. In recent years, a method that is easier and more effective than pollination with a bamboo skewer has been developed in production practice: Press the male flower petals to the fruit stalk to expose the stamens, and lightly touch the side with dense pollen to the female stigma. Investigations have found that the same species of plant, the winged Luohanguo, is highly resistant, has large fruits, and a high yield, making it a good material for breeding. Moreover, individual plants have bisexual flowers that bear fruit without human intervention, which is an atavistic phenomenon that provides insight into the evolution of angiosperms. Further research is needed on the winged Luohanguo, which has bisexual flowers, in order to solve the problem of Luohanguo&#受粉のための人間の介入への39の依存。
栽培環境が破壊され、ナハングクの生殖質が深刻に悪化しているため、ナハングクの生殖質革新が必要だ。
多倍育種技術を新品種の研究開発に応用することは、従来の品種の欠点を克服する効果的な方法だ。単糖の皮と果肉の果物では存在するが、汽笛)どんなにいい役者なく単糖类が大量の特許油を含みますが大幅に増え抽出の難航や禊(みそぎ)や制作費をつぎ込み、したがって、繁殖種無しLuohanguo一般品種より単糖という高いな内容と実の全体利用率高くまで工業の発展の記録を立てるLuohanguo全体のいる。
参照:
[1]国民薬局方委員会'の中国の共和国。ピープルの薬局方'の中国共和国(パートi) [m]。北京:中国医学科学技術出版社、2010年。197.
【2】李デン鵬、張鴻瑞。羅漢国、広西の専門工場の研究と応用[j]。^『仙台市史』通史編2、通史編2、273 -276頁。
【3】李健強、呉正一、陸安民。cucurbitales亜科植物の細胞学的観察[j]。1993年雲南植物研究15(1):101-104。
【4】荘偉健、林智良、鄭神坤。羅漢国の染色体の種類の研究[j]。植物日刊热帯および亜热帯1997年、5 (2):~ 25
[5]ゾウ在りけり」。4つの植物の花粉の観察:羅漢国、穆baizi、ku gua、河南chi jing ying [j]。1981年広西植物学((3))8月1 28。
【6】陸安民、張志雲。中国のluohanguo植物[j]。^『仙台市史』通史編1、通史編1、通史編4、27-33頁。
[7] zhou liangcai, zhang biyu, qin liang, et al。羅漢国の品種と資源の調査と活用[j]。1981年広西植物学((3))8月1 29-33。
[8]仲石垣。羅漢国の研究状況[j]。^『仙台市史』通史編4(通史編4)166 -166頁。
【9】何金王、秦正偉、李伯林。羅漢国の新品種「宝林3号」の高収率栽培技術[j]。2007年農業広西チワン族誌第22(1):46-47、62に。
[10] ma xiaojun, mo changming, bai longhua, et al。羅漢国の新品種、永慶1号[j]。^『仙台市史』第35巻(仙台市史)、1855年。
[11] li feng, jiang hanming, jiang xinneng, et al。羅漢国組織培養苗の栽培に関する研究[j]。^『仙台市史』通史編4(通史編3)359-363頁。
[12] fu changliang, ma xiaojun, bai longhua, et al。羅漢国無ウイルス苗の急速な増殖に関する研究[j]。中国漢方薬,2005,36(8):1225-1229。
[13]朱田んぼや畑。平野のシライチア・グロブノリの栽培技術に関する議論[j]。^『仙台市史』通史編、通史館、2004年(平成16年)3月15日、13-14頁。
[14] matsumoto k, kasai r, ohtani k, et al。小ククルビタン(cucur-bitorii)の果実から得られる糖体[j]。1990年(平成2年)化学Pharmブル38(7):2030-2032。
【15】楊秀偉、張建業、銭仲明。siraitia grosvenorii産の新しい天然サポニン[j]。^ a b c d e f g h『仙台市史』、2008年、39(6)、810-814頁。
[16] wang yaping, chen jianyu。siraitia grosvenorii [j]の化学成分に関する研究。^『仙台市史』第2巻、仙台市、1992年(平成4年)、62頁。
[17] si jianyong, chen dihua, chang qi, et al。羅漢国におけるトリテルペノイド配糖体の単離と構造同定[j]。^『仙台市史』通史編4(通史編6)489-494頁。
[18] wang xuefen, lu wenjie, chen jiayuan, et al。羅漢國根の化学成分の研究(i) [j]。中国の漢方薬,1996,27(9):515-518。
[19] si jianyong, chen dihua, shen liangang, et al。広西の特産植物である羅漢國根の化学成分に関する研究[j]。1999年日刊薬学34(12):918-920。
【20】徐偉坤、孟梨山。羅漢国[j]のタンパク質含有量の決定。1986年植物広西チワン族6(3):295-296。
[21] si jianyong, chen dihua, chang qi, et al。羅漢国におけるフラボノイド配糖体の単離と構造決定[j]。1994年日刊薬学、29(2):158-160。
[22] chen quanbin, yang jianxiang, cheng zhongquan, et al。羅漢国(siraitia grosvenorii)由来フラボノイド配糖体の分離と構造同定[j]。^『仙台市史』通史館、2006年(平成18年)3月1日、35-36頁。
[23] liao riquan, li jun, huang xishan, et al。羅漢国の化学組成に関する研究[j]。^ a b c de f g h『仙台市史』通史館、2008年(平成20年)6月28日、125 -125頁。
【24】徐維坤、孟梨山、李仲耀羅漢国におけるマンニトールの分離と同定[j]。1990年(平成2年)植物広西チワン族10 (3):254-255
[25] meng xialin, zhou qi, rong xiaoyi, et al。羅漢国の無機元素の決定と分析とそのルーツ[j]。^『仙台市史』通史編、仙台市、1989年(平成元年)12月6日、62頁。
【26】徐維坤、孟梨山。羅漢国の栄養成分の決定[j]。広西チワン族自治植物、1981年、1(2):50-51。
[27] cheng juying, luo silian, pan yufa, et al。広西チワン族自治区植物の油の研究:i . 50種の種子の油組成[j]。^『仙台市史』通史編2(通史2)、26-33頁。
[28] wang ting, huang zhihong, jiang yimin, et al。モンクフルーツ甘味糖体の生物活性に関する研究[j]。^『仙台市史』通史編1、通史編13、通史編13、通史編13、通史編13、通史編13、通史編13。
【29】蘇環群陳在義羅漢国の薬理学と応用研究[j]。^『官報』第726号、大正10年(1926年)7月7日。
【30】葉敏、周英。羅漢國の葉茎エタノール抽出物の静菌効果[j]。2008年山岳農業のバイオロジー、27(1):42-46。
[31] wang q, wang c, dai s, et al。羅漢果スイートサポニンのマウス細胞免疫機能に対する調節効果[j]。^ a b c d e f g h『中国の歴史』、2001年、24(11):811-812。
[32]木島武。羅漢國の甘味物質の抗がん効果[j]^ a b c d e f g h『東洋医学』、2003年、25頁。
[33] zhang liqin, qi xiangyang, chen weijun, et al。羅漢國エキスの抗酸化活性に関する研究[j]。2006年食物科学専攻、27(1):213-216。
[34] wei rongchang, li feng, huang xiyang, et al。pcr-rflpパラメータの多倍数性luohanguoに対する最適化と応用[j]。2009年広西植物学、29(6):889-893。
【35】周俊雅唐紹慶栽培luohanguoの遺伝的多様性のrapd分析[j]。分子植物育種,2006,4(1):71-78。
[36] huang jiang, jiang huiping, chen tingsu, et al。羅漢国の異なる生殖質の遺伝的関係に関するrapd分析[j]。2006年(平成18年)3月1日-1号機が完成。
[37] wei suling, huang zimei, yang hua, et al。羅漢国における性関連rapdマーカーのクローンと配列解析[j]。^岩波書店、2008年、47(3)、251-253頁。
[38] wei rongchang, li hong, jiang jiangang, et al。種子のない羅漢国とその両親の遺伝的背景に関するissr分析[j]。^「the journal of horticultural science, 2012, 39(2): 387-394。
[39] tao li, wang yuejin, you min, et al。aflpは、シライチア・グロブノリアのdna指紋地図を構築し、その苗の性別を特定するために使用されます[j]。^『岡崎市史』岡崎市史編纂委員会、2005年(平成17年)、77-80頁。
[40] liu l h, ma x j, wei j h, et al。issrマーカーとsrapマーカーに基づくluohanguo (siraitia grosvenorii)の最初の遺伝的連鎖地図[j]。^ a b c d e f g h i(2011) 54 -25頁。


 英語
英語 フランス
フランス スペイン
スペイン ロシア
ロシア 韓国
韓国 日本
日本




