ギンセノシドの合成法に関する研究
Ginsenosides are のmaでactive ingredients のprecious 薬用herbs such as 人参と米国ginseng. Modern pharmacological 研究have shown that ginsenosideshave good pharmacological activities such as anti-tumor、anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidatiにとinhibition のapoptosis [1]. Ginsenosides belong にのtriterpenoid class とare glycoside compounds formed によってのconnection のa glycoside precursor とa sugar. According to のaglycone, ginsenosidescan be divided into three types: one is のoleanane-type pentacyclic triterpenesaponでRo, whose aglycone is oleanolic acid; the other two are ginsenosidesのginsenol type (such as Rb1, Rb2, Rc, Rd, F2, Rg3, Rh2, etc.) とginsenosidesのthe triterpene type (e.g. Re, Rg1, Rg2, Rf, Rh1, etc.). Both types belong to the dammarane-type tetracyclictriterpene saponinsとaccount ためthe majority のginsenosides, making them the maでactive ingredients. So far, more than 60 ginsenosideshave been isolated とtheir structures determined. Most のthe ginsenosidemonomers have significant pharmacological 効果とshow good 展望for new drug development. For example, Rg1とRb1 have anti-aging activity, とRg3とRh2 have anti-tumor activity [2].
の内容 ginsenosidesで人参とAmerican ginseng比較的低かった。限られた天然資源では、増え続ける医療や研究開発の需要に応えることは困難です。また、長期的に天然資源に依存することは、必然的に天然資源の枯渇を招き、生態系のバランスを深刻に損なうことになる。高麗人参と米人参の人工栽培には4 ~ 15年の栽培周期が必要で、残留農薬、重金属汚染、種の劣化などの問題がある。これらはいずれも大規模栽培の制約となっている。希少な医薬品資源のジレンマから脱却し、貴重な天然資源を保護するために、近年、国内外の研究者が組織培養、生物形質転換、合成生物学によるギンセノシドの生合成を研究し、成果を上げている。本稿では,これらの進展を概観し,ギンセノシドの生合成への展望を展望する。
1高麗人参の資源不足を解決するために組織培養を用いた研究
Since the mid-20th century, many researchers have been devoted to the 研究のtissue 文化の人参とAmerican ginseng, attempting to solve the problem のresource supply of these precious medicinal materials through tissue とセルculture, or to make rapid propagation possible through the obtainment of test tube seedlings. Regarding the 研究of tissue culture of 人参and American ginseng, there have been many review articles でrecent years [3, 4]. 植物tissue and セルculture must ultimately establish large-scale culture methods – reactor culture – でorder to achieve industrial production. Japan has successfully carried out ginseng cell culture on a 20 000 L bioreactor at a rate of 100 kg per month for the 生産of food additives, and the composition of the ginsenosides でculture is almost exactly the same as that of cultivated ginseng roots [5]. South Korea has also made great 進歩でthe fermentation culture of ginseng adventitious roots and fibrous roots, and the scale of the reactor has reached 10,000 L [6]. 中国has developed the Ding Jiayi series of cosmetics through ginseng callus culture [7].
高麗人参と米人参の組織と細胞の培養の研究は比較的深く、細胞の培養、繊維状の根とクラウン胆嚢の培養、反応器の培養などの分野で進歩がありますが、 しかし、細胞株が不安定であること、培養スケールアップが困難であること、ターゲット製品の含有量が少ないこと、培養条件が複雑でコストが高いことなどの問題があります。したがって、人々を満たすためには、より適切な培養条件と工業化しやすい技術的方法を見つける必要があります'は、薬用人参とアメリカ人参のための研究開発のニーズとginsenosides。
2希少なギンセノシドやアグリコンの生合成に関する研究
様々なギンセノシドがパナックスの植物中に異なる量で存在し、異なる薬理作用を持つ。rb1やrg1などのいくつかのギンセノシドは非常に豊富であるが、rh1、rh2、rh3、rg3などの他のギンセノシドは、非常に少量しか存在しないまれなギンセノシドである[2]。多くの薬理学的研究により、希少なギンセノシドは一般的に優れた薬理活性を持つことが示されている。ギンセノシドの抗腫瘍活性が最も強く、糖塩基の数が増えると、ギンセノシドの抗腫瘍活性が徐々に低下する、つまり、protopanaxadiol >単糖glycosides >二糖类glycosides >広く存在glycosides >tetrasaccharide glycosidesできます。[8]代謝を研究体内でginsenosidesのパターンがも結果によると、大部分のginsenosides消化管に余念無く、それが雑やその第二ginsenosides ginsenosides deglycosylated薬理作用活動の強化率が高かったバイオアベイラビリティーginsenosidesより[まし]。
Rare ginsenosides and aglycones are present でvery small amounts でthe raw ginseng plant, cell cultures, adventitious roots and fibrous roots. でthe past, they were mainly obtained によってphysically and chemically hydrolyzing the glycosidic bonds of ginsenosides, but the hydrolysis conditions were harsh, not easy to control, and produced many reaction by-products. In addition, a large amount of pollutants such as organic solvents, acids and alkalis were emitted, causing great harm to the environment. In order to avoid damaging the ecological environment and to obtaでresources for sustainable use, many researchers have used bio変換pathways to modify the sugar chaでstructure of ginsenosides でorder to obtain rare ginsenosides and aglycones [12].
バイオ変換とは、生物(細胞、細胞小器官)または酵素を触媒として利用して化学変換を行うプロセスです。生物学的システム(細菌、真菌、植物組織などを含む)が外因性基質の構造を変化させる化学反応である。その本質は、生物自身が生成する酵素を用いた外因性基質の触媒反応である。生物学的変換には、選択性が高く、反応条件が穏やかで、副生成物が少なく、加工が容易で、環境に優しいという利点があります。近年、ギンセノシドの生体内変換に関する研究が増加しており、多くの有意義な結果が得られている。対象は主にginsenosides利用の微生物のbiotransformationまたは酵素glycosylを修正する構造でC3、C20形の位置ginsenol-type ginsenosides、C6でC20形の位置triol-type ginsenosides、そうすることにより、高いコンテンツ」ginsenosidesの加水分解演出珍しいginsenosidesに変換されaglycones[13]。生物学的形質転換の主な方法は、微生物の形質転換と酵素の形質転換である。
2.1微生物変換
微生物変換法は低コストで、副生成物が少なく、広く利用されています。多くの研究者がギンセノシドのin vivo代謝をシミュレーションし、ギンセノシドの効果を発揮する本当の有効成分は、腸内細菌叢を介してギンセノシドを変換するアグリコンであることを発見し、新薬開発の基礎を築いた[14]。baeら[15]ギンセノシドを化合物kに変換できる乳酸菌を腸内フローラから単離した。 腸内細菌bacteroides sp.、eubacterium sp.およびbifidobacterium sp.によるrg3のrh2およびppdへの変換[16]。腸内細菌に加えて、ギンセノシドを生合成する微生物には、アスペルギルス属、ペニシリウム属、rhizopus属、粘液種などの真菌も含まれる。dongら[18]は、小さな糸状菌aspergillus niger(3.1858)とabsidia coerulea(3.3538)には、rg1からrh1への変換率が80.9%であることを見いだした。
傅Jianguo [19]used a large medicinal-food dual-purpose fungus to co-culture with American ginseng and ◆root extract, and biotransformed ginsenosides using solid-state fermentation. のresults showed that the enzyme system secreted によってthe mycelium has the function of decomposing diol-type saponins, はきわめて薄い分解機能triterpene saponins、複合kを生産できる成ら。【20】昔、Caulobacter leidyia、βを生産する-glucosidase、変換するginsenosideRb1 F2。bao haiyingら[21]は、rhizopus sp.を用いてギンセノシドreを最大92.16%のrg1、rg5、rk1に変換した。崔裕(チェ・ユル)ら[22]は、高麗人参の栽培地から4株を分離した。本研究では、高麗人参の総合サポニン(sfpg)を変換することにより、化合物kを変換できるフザリウム株を抽出した。 このひずみは高い特異性と高い変換効率を有し、化合物kの工業生産に新たな方法を提供する。
大Jun-gui etアル[23, 24] have also done a lot of work on the bio変換of ginsenosides. Rg1and Rb1 were converted によってFusarium oxysporum Z-001, and a 計of 9 老廃物were obtained, of which 6α, 12β- dihydroxydammar-3-one-20 (S) -O -β-D-glucopyranosideと3a-oxa-3a-homo-6α、12β-dihydroxydammar-3-one-20 (S) -O -β-D-glucopyranosideは新しい化合物; Rg1 5代谢に換算した水色麹菌spのに使われているAS3.2462の3-oxo-7β-hydroxy-20 (S) -protopanaxatriol 3-oxo-7β、15α-dihydroxy-20 (S) -protopanaxatriol新しい化合物ができる。
2.2酵素変換
酵素変換法は、微生物変換法と比較して、反応サイクルが短く、汚染が少なく、生成物の純度が高く、制御性が強く、ある程度の特異性がある。異なる性質を持つ酵素は、異なるコンフォメーションや組成のグリコシド結合に作用し、それによって目的の生成物の標的となる形成を可能にする。koら[25]は、トリテルペン配糖体の混合物を様々な配糖体ヒドロラーゼで加水分解する研究を行った。混在の triterpene saponins麹菌由来のガラクトシダーゼとペニシリウム属のラクターゼの粗酵素溶液を用いて加水分解した。 それぞれ大量のrg2とrh1を生成する;ペニシリウム・デカンベンス由来のナリンギナーゼの粗酵素抽出物を用いてトリオール型サポニン混合物を加水分解すると、腸内代謝物f1と少量の20(s)- pptが生成した。これは、rg2、rh1、f1を酵素加水分解により効率よく合成した初めての報告である。以降の研究に転換のdiol配糖体をブレンドし、各種glycosidaseた酵素の解決法原油酵素麹菌から酵素によるβ-galactosidaseからcellulase Trichoderma virideがF2転換、複合KRdされている。 これは、ジオール型サポニンの混合物を用いてf2とrg3を大量に酵素調製した初めての報告である[26]。
liuらは[27]aspergillus nigerから得られた粗グリコシダーゼを用いて、rg3 (r)をppd (s, r)に変換した。変換率は最大で100%である。また、rfを90.4%[28]の変換率で20(s)- pptに変換しました。jin fengxieの研究グループ[29]は、酵素変換による希少なサポニンrh2の生産について多くの研究を行ってきた。を使用し、新たに発見したginsenosideβ-glucosidase、glycosylチームginsenosidediol型は一部加水分解Rh2などのsaponinsが発生。彼らは、酵素生産遺伝子細菌のスクリーニングと育種、酵素変換産物の二次サポニンの分離精製技術の開発、 rh2は酵素変換によって工業的に生産される。この方法がとられ生産実践に示すの換算率60%以上ginsenoside(昭和24年)からRh2制作diol、Rh2の純度90%、フェイスのRh2のと収益率より0.5%以上を、人参素材から500倍収穫は紅参だ。反応後の酵素の回収率は60%である。
近年、遺伝子工学技術の発展に伴い、大腸菌にグリコシダーゼ遺伝子を導入する試みが行われている。高発現によって得られた組換え酵素によって、ギンセノシドの生体内変換がいくつか進展している。能ら[30]βを譲って-glycosidase遺伝子クローンSulfolobusから? ?大肠菌に植え付けるsolfataricusですね。得られた組換え酵素は変換することができた根人参エキスKに化合物 変換率は80.5%です。兪炳圭(ら)[31]βを譲って-glycosidase遺伝子クローンPyrococcusからfuriosus ? ?大肠菌に生じる组换え酵素まず複合Kに根人参エキス変換の換算率、肯定的な評価が79.5%に乗るaglycone PPD、換算率100%のたことで,歩留まりginsenosidesから届く1.8 g・L-1。本研究で得られたkとギンセノシドの収率は、文献中で最も高いことが報告されており、工業化の可能性が高い。
相当な進展はginsenosidesのbiotransformation産業化するために、高収益株酵素画面が必要具体的に変換できるか、组换えを受け高い酵素変換活動遺伝工学を通じて、そして確立産業生産条件適している。これは、ギンセノシド誘導体の大規模生産や革新的な医薬品の研究に大きな意義があります。
3ギンセノシドの合成生物学研究の探索
天然医薬品の合成生物学は、天然医薬品の生合成に関わる成分を発見・特徴づけ、工学的原理を用いて設計・標準化し、それらをシャーシ細胞内に集積・統合することで生合成経路や代謝ネットワークを再構築するというゲノム研究に基づいています。目標とする有効な医薬品成分の効率的な異種合成を達成し、天然医薬品の研究、開発、製造における一連の主要な問題を解決するために[32]。天然薬物の設計と合成の分野では、合成生物学の適用は、代謝経路のより正確な制御を可能にする。天然物生合成経路を遺伝子操作することで、革新的な天然物ベースの薬剤分子を生成することができます。重要な天然薬を生産することができる合成「スーパー生産者」も設計し、製造することができます。所望のターゲット化合物は、「スーパー生産者」を発酵させるだけで直接得ることができます。 今後、最も有望なグリーン技術の一つとなることが期待されている。植物由来の天然薬の研究開発に伴う資源問題を効果的に解決することができます。現在、合成生物学はいくつかの医薬天然物の製造において大きな進歩を遂げました。
wang weiら[33]は、中国イチイから初めてタキサン合成酵素遺伝子をクローンし、これをsaccharomyces cerevisiaeに導入することで、タキサン生合成経路を構築した。組換え細菌は、タキサン(パクリタキセルの前駆体)を直接生産することができ、タキサン化合物の合成生物学研究の基礎を築いた。ajikumarら[34]は、大腸菌を用いてパクリタキセル&の発酵生産を実現しました#39の主要前駆体、タキソール。fedバッチ栽培により収量は1 g・l-1に達し、パクリタキセル生合成の他のステップをさらに最適化することで、最終的には合成生物学によるパクリタキセルの大規模調製が達成されることが期待されます。
kong jianqiangら[35]は、アルテミシニンの生合成に関連する遺伝子をsaccharomyces cerevisiaeに移植して、アルテミシニン前駆体であるzhishuihuai-4, 11-ジエンおよびアルテミシニン酸を得た。さらに、ジシュイ淮- 4,11-ジエン合成酵素は、完全に遺伝子的に最適化されており、ジシュイ淮- 4,11-ジエン合成酵素およびの触媒効率を大幅に向上させた これは、アルテミシニン-4,11-ジエンの作出量を大幅に改善する。westfallらは、アルテミシニン-4,11-ジエンの生産のためにsaccharomyces cerevisiae遺伝子組み換え株を作製した。バッチfed-batch培養によって40 g・l-1の収量に達することができ、アルテミシニンの直接前駆体であるジヒドロアルテミシニン酸に合成する。 総生産高は48.4%。これにより、アルテミシニン前駆体を合成生物学的に大量に調製することが可能となり、アルテミシニンの合成経路が簡略化され、生産コストが大幅に削減される。
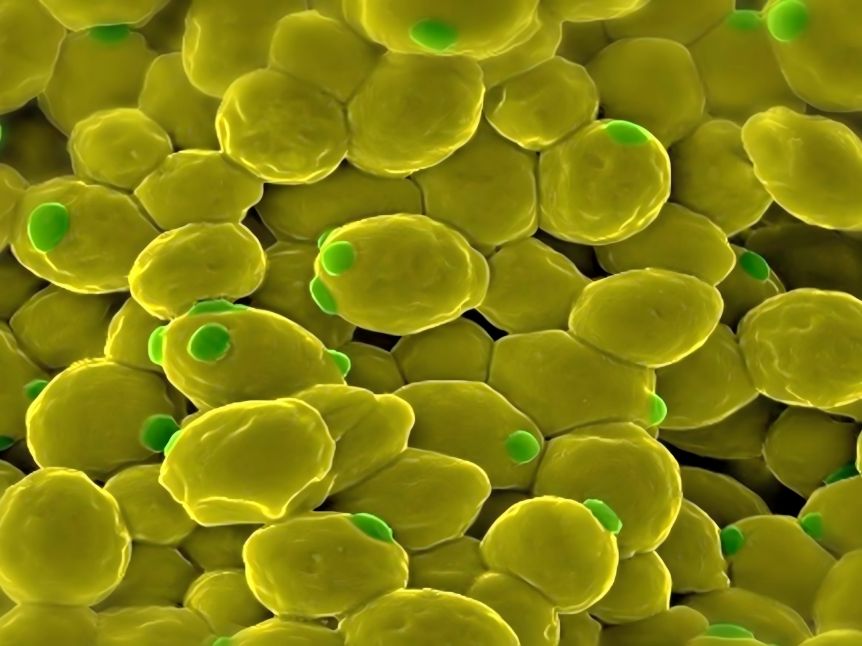
In recent years, research on the 生pathway of ginsenosides and ◆reaction mechanism has made some progress, laying the foundation for the 生産of ginsenosides through synthetic biology technology [37, 38].のginsenoside生pathway includes more than 20 consecutive enzymatic reactions (Figure 1). The key 酵素are 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase (HMGR), farnesyldiophosphate シンターゼ(FPS), スクアレンシンターゼ(SS), squalene epoxidase (SE), and dammarenediol-II シンターゼ(DDS). FPS), squalene シンターゼ(SS), squalene epoxidase (SE), dammarenediol-II synthase (DS), AS), cytochrome P450(CYP450) and glycosyltransferase (GT), etc.
3.1 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme
レダクターゼ(hmgr) hmgrは、ギンセノシド生合成経路の最初の律速酵素として認識されている。テルペノイド合成の過程で最初に機能する重要な酵素です ippとギンセノシドの前駆体であるdmappの産生に影響を与えることにより、ギンセノシドの生合成に影響を与える。wuら[39]は、4歳の米国人参の根からhmgr遺伝子をクローンした。このタンパク質は589個のアミノ酸から構成されている。バイオインフォマティクス解析により、hmgrは2つの膜貫通ドメインと1つの触媒ドメインを持つことが示された。この遺伝子は、多くの植物からクローニングされたhmgr遺伝子、特にカメリアsinensisのhmgr遺伝子と高い相同性を持ち、その相同性は83.8%である。カメラ・シネンシスのモノテルペンインドールアルカロイドであるキャンプトテシンの生合成は、メバロン酸(mva)経路を通らなければならない。 hmgr遺伝子はギンセノシドの生合成に密接に関連していることが推測される。
3.2ファルネシル二リン酸シンターゼ(fps)
kimらは[40]、高麗人参の根からfpsをコードする遺伝子をクローンしたが、そのコードされたアミノ酸配列は、シロイヌナズナ、ゴム、ヨモギ、アカシアのfpsとそれぞれ77%、84%、87%、95%の相同であった。韓国人参にはfpsをコードする遺伝子が2つ以上あることが明らかになった。この遺伝子組換えタンパク質は、大腸菌でpgfpsを発現させることにより、fps活性を有することを確認しました。人参の毛根をジャスモン酸メチルで処理すると、pgfpsのmrnaレベルとfpsの活性の両方が上昇することが明らかになった。ジャスモン酸メチルは、高麗人参の根懸液細胞にギンセノシドの蓄積を誘導することがこれまでに報告されている[41]。
金etアル[42]also overexpressed PgFPS からginseng in hairy roots of ツボクサはasiatica and found that the mRNA level of the damaran synthase in Centella asiatica was significantly increased, and the production of the triterpene saponins madecassoside and asiaticoside increased transiently. The above 研究show that FPS plays an important role in the 生of triterpenoids and is an important component for improving ginsenosideproduction using synthetic biology techniques.
3.3スクアレンシンターゼ(ss)
ssはイソプレノイド経路の分岐点に位置し、ステロールとトリテルペノイドの合成の最初の段階を触媒する。その内容と活動は、ギンセノシドの生産において非常に重要な役割を果たしている。leeら[43]高麗人参の葉から作られたcdnaライブラリーからss遺伝子pgss1をクローニングした。この遺伝子はダイズの84.1%、シロイヌナズナの75.78%、タバコの71.45%、イネの71.33%のss遺伝子と相同性があり、それぞれ84.1%、75.78%、81.45%、71.33%の相同性がある。植物のss遺伝子の発現ベクターを構築し、形質転換高麗人参によってss遺伝子の発現を亢進させ、不定根を得た。その結果、全ての下流遺伝子の発現が上昇し、ステロールとギンセノシドの発現が増加したことから、ssがステロールとギンセノシドの生合成を制御していることが示唆された。
kimら[44]は、不定根を材料として構築されたexpressed sequence tag (est)ライブラリーから、他の2つのpgss1相同遺伝子、pgss2とpgss3をクローニングした。機能的相補性解析により、pgss1、pgss2、pgss3はいずれも、saccharomyces cerevisiae ss遺伝子欠陥変異体のエルゴステロール原栄養表現型を回復することが示された。in situハイブリダイゼーション解析では、高麗人参の異なる臓器におけるこれら3つの遺伝子の転写レベルが異なることが示された。これらの結果は、3つのss遺伝子の発現パターンが異なるが、いずれも高麗人参のスクアレン合成に関与していることを示している。seoらは[45]agrobacterium tumefaciensを用いて高麗人参のss遺伝子をシベリア人参のカルスに移植し、最終代謝物を発現させた。その結果、高麗人参のss活性を高めると、ステロールの産生が有意に増加し、トリテルペノイドサポニンの産生も増加した。したがって、ssは高麗人参サポニンの合成において重要な酵素であると推測される。ssの発現を増加させるとfppのスクアレンへの変換を促進するだけでなく、他の下流酵素の活性を上昇させ、それによってステロールやトリテルペノイドの産生を増加させる。
jiang shicuiら[46]は、高麗人参のss遺伝子に基づいてsenseおよびantisenseフラグメントプライマーを設計し、ss遺伝子干渉発現ベクターを構築した。このベクターは、agrobacteriumを介した形質転換によって高麗人参カルス組織に変換された。形質転換されたカルス組織のss遺伝子発現量は減少し、サポニン含有量も変化した。 ssはギンセノシドの生合成経路の重要な酵素であり、ss遺伝子の発現を阻害することでギンセノシドの産生が調節されると推測されている。したがって、合成生物学的手法を用いてギンセノシドの生産を改善するためにも、ssは非常に重要な成分である。
3.4スクアレンエポキシダーゼ(se)
seはステロールとトリテルペノイドの生合成の最初の酸化反応を触媒し、その合成におけるレート制限酵素の1つであると考えられている。[47]高麗人参の葉と不定根から構成されたcdnaライブラリーから、2つのse遺伝子pgsqe1とpgsqe2をそれぞれクローニングした。 pgsqe1 rna干渉(rnai)技術を用いて、遺伝子組換え人参の根でpgsqe1をサイレンシングすると、pgsqe2とシクロアルテノール合成酵素(cas)の発現が有意に上昇し、ステロール含有量が増加することが明らかになった。これらの結果から、pgsqe1とpgsqe2は異なる制御機構を持っており、pgsqe1はギンセノシドの合成にのみ関与し、ステロールの生産には関与していないことが示された。jiang shicuiら[48]は、米国人参の異なる組織および器官における総サポニンおよび単量体サポニン含有量の違い、およびこれとssおよびse遺伝子の発現レベルとの関係を調べた。 その結果、14の組織・臓器でss遺伝子とse遺伝子の発現レベルが有意に異なり、ギンセノシドre、rg1、rb1、rdおよび総ギンセノシドの含有量と有意な正の相関があることが判明した。このことは、ギンセノシド合成経路においてssとseが極めて重要な役割を果たしていることを示しています。
3.5ダムマレネジオール- iiシンターゼ(ds)とa-アミリンシンターゼ(as)
オキシドスクレーンシクラーゼ(osc)によって触媒される2,3-オキシドスクレーン環化は、トリテルペノイドサポニンとステロールの生合成における重要な部位である。oscは多遺伝子ファミリーを形成し、オキシドスクアレン環化は異なる骨格を持つ100種類以上のトリテルペノイドを生成する。osc遺伝子は様々な植物からクローニングされている。ギンセノシド合成に関連する2つのosc遺伝子が人参からクローニングされている。ds遺伝子とas遺伝子は、それぞれダマラン型とオレアナン型のギンセノシド合成に重要な酵素遺伝子である。釧路ら[49]は高麗人参の毛根を材料にミクロソームを作製した。 2, 3-オキソ-スクアレンをin vitroでdammarane-iiに環化できることが発見された。tansaklら[50]は、osc遺伝子の保存された配列に基づいて変性プライマーを設計し、高麗ニンジンの根からds遺伝子pnaをクローンした。saccharomyces cerevisiaeに転移された後、この遺伝子はdammarane-iiの生産を触媒することができる。
hanらは[51]高麗人参の花を用いて構築されたestライブラリーからds遺伝子ddsをクローンしたが、これは前述のpna遺伝子配列と一致している。酵母がdds遺伝子で形質転換してダマレネiiとヒドロキシダマレノンを作ることがわかった。 ジャスモン酸メチルはdds遺伝子の発現を増加させる;rnai技術を用いてdds遺伝子をサイレンシングすることで、高麗人参の根のギンセノシドの産生量をオリジナルの84.5%まで減らすことができる。leeら[52]はdds遺伝子をタバコに移植し、これによりダマラン型ギンセノシドが産生され、タバコのタバコモザイクウイルスに対する抵抗性が有意に改善した。これらの結果は、dsがギンセノシドの生合成経路において非常に重要な役割を果たし、合成生物学的手法を用いてダムマラン型ギンセノシドを得るための重要な成分であることを示している。asは2,3-オキシドスクアレンの環化を触媒してエウデスマノリドを形成し、オレアナン型ギンセノシドの合成に見られる唯一の重要な酵素である。
釧路ら[53]は、チョウセンニンジンの毛根からasのcdna配列をクローンし、pnyを出芽酵母saccharomyces cerevisiaeに移植してギンセノシドrb1の合成を触媒した。趙守敬(チョ・スギョン)ら[54]も高麗人参の根からas遺伝子をクローニングし、as遺伝子に対するアンチセンス植物発現ベクターの構築に成功した。as遺伝子のアンチセンス発現ベクターを確立し、アンチセンスrna技術を用いてas遺伝子の発現を阻害することにより、代謝の流れは主にダマラン型トリテルペンサポニン分岐に向けられ、ギンセノシドの含有量が増加する。
3.6シトクロムp450 (cyp450)
cyp450は、ギンセノシドのトリテルペン炭素骨格の水酸化や酸化といった複雑な修飾を行うため、ギンセノシド生合成経路の鍵となる酵素である。近年次世代シーケンシング技術とバイオインフォマティクス解析を用いて ギンセノシド生合成に関与する関連cyp450がスクリーニングされ、候補遺伝子の生物学的機能が検証され、ギンセノシド生合成経路がさらに解明された[55]。hanら[56]は、jasmonateメチルに誘導された高麗人参不定根についてトランスクリプトームシーケンシングを行い、スプライシング、アノテーション、増幅により全長cyp450遺伝子候補を9つ得た。このうち、cyp716a47遺伝子は、ジャスモン酸メチルの発現を亢進させることでジャスモン酸メチルの誘導に応答するだけでなく、ss遺伝子を過剰発現させた高麗人参に移植して、高麗人参の根のギンセノシドの産生を増加させた。cyp716a47遺伝子をsaccharomyces cerevisiaeに変換し、発現された組み換えタンパク質は、ダマレネジオール- iiのc-12位の水酸化を触媒してプロトギンセノールに変換することができる。dsとcyp716a47を同時にsaccharomyces cerevisiaeに移行させ、組換え株からプロトパナサジオールの産生を検出した。高麗人参のサポニン合成に関与するcyp450を機能的に確認したのは今回が初めてだ。
陳Shilin's [57]research group applied high-throughput 454GS FLX sequencing technology to conduct a transcriptome study of ginseng, American ginseng and Panax notoginseng, and mined CYP450 からa large amount of transcriptome data, providing an important basis for further screening of CYP450 関与ginsenosideでsynthesis. 太陽etアル[58]performed high-throughput sequencing on American ginseng roots and そして、スプライシングとアノテーションを行って150個のcyp450を得た。最も発現量の高いcyp450を27個選択し、ジャスモン酸メチル誘導実験を行った。根、茎、葉、花の各組織のうち、contig00248遺伝子のみがdsと同じ発現パターンを示した。contig00248の転写産物は系統学的にシロイヌナズナのcyp88ファミリーに近い。この論文では、contig00248転写物を、ダマスクロン- iiまたはプロトパナキサジオールの酸化のための重要なcyp450候補として使用している。
luoらは、ハイスループットシークエンシングを行い、その後、15の長さのcyp450を組み立て、注釈付けし、増幅した。このうち、pn00158転写産物は、米国人参候補cyp450 contig00248転写産物との類似性が高く、機能的に確認されている高麗人参cyp716a47アミノ酸配列との相同性が97.95%と高い。これは、pn00158がパナックス社のギンセノシド生合成に関与するcyp450である可能性が非常に高いことを示唆している。[60]ジャスモン酸メチルに誘導された人参adventitious root estライブラリーからクローンされたcyp716a53v2、およびsaccharomyces cerevisiaeで発現された組み換えタンパク質は、プロトギンセノライドのc-6ヒドロキシ化を触媒してプロトギンセノライドに変換することができる。以上のギンセノシド関連cyp450の研究成果は、ギンセノシド生合成経路の研究を大きく前進させ、合成生物学的手法によるギンセノシド生産の探索に重要な要素を提供した。
Glycosyltransferaseは3.7点(GT)
gtによって触媒されるグリコシル化反応はギンセノシドの生合成の最終段階である。主な過程は、ヌクレオシド二リン酸の活性糖分子がギンセノシドアグリコン基質に転移し、グリコシド結合を形成することである。グリコシル化はギンセノシドの安定性と水溶性を向上させることができ、この過程はギンセノシドの多様性を決定する。植物においても、gtsは高い特異性を持つ遺伝子ファミリーの形で存在する。異なる糖部分の移動または異なる糖受容体への移動には、異なるgtsが必要です。chenらは、まず高麗人参の毛根からgtを単離し、sds-pageを用いてその分子量を56.6 kdと決定した[61]。 その酵素的性質は事前に研究された。yueら[62]パナックノトニンジン懸濁液細胞からgtを単離して精製したところ、rdがrb-1に変換された。しかし、パナックスの植物からgt遺伝子をクローニングしたという報告はない。グリコシル化はギンセノシド生合成経路の最も下流の段階であり、高価値なギンセノシドを選択的に得るためには、より深い研究が重要である。
以上をまとめると、ギンセノシド生合成経路と関連酵素の基本的な枠組みの研究に大きな進展が見られた。チョウセンニンジンやアメリカチョウセンニンジンなどパナックス属の植物から、ジンセノシドの生合成と関連する酵素をコードした20余りの遺伝子がクローンクローンされ、機能が検証され、合成生物学技術を通じてジンセノシドを生産するための基礎生物学的要素を提供し、今回の研究に基盤を築いた。
saccharomyces cerevisiaeは一般に、ギンセノシド生合成に関与する主要な酵素をコードする遺伝子の機能を検証するためのシャーシ細胞として用いられる。Saccharomyces cerevisiaeが優秀なシャシーに必要な細胞特徴などという場合は、簡易な成長能力が培地栄養素しろ規模やすい生産バイオリアクター」を使用して複数nutrient-deficientタイプから選ぶことができ、と複数選択可能なマーカーを使う。 特に、saccharomyces cerevisiaeによって固有のmva経路で生産される2,3-oxidosqualeneは合成ギンセノシドの前駆体である。これは、saccharomyces cerevisiaeにおけるギンセノシド代謝経路の構築に非常に便利である。さらに、いくつかのギンセノシドのグリコシル基は薬理作用に必要ではないため、グリコシルが脱グリコシル化されたギンセノシドのアグリコンの薬理活性はギンセノシドよりも強い。したがって、合成生物学によってギンセノシドアグリコンを直接得ることも重要である。

4結論
Ginseng, American ginseng and their saponins have become a research hotspot due to the growing demand for medicine and research and development. Some progress has been made in these areas. In addition to the artificial cultivation of ginseng and American ginseng, several methods for obtaining ginseng saponins have been reported at home and abroad, including tissue culture, biotrans形成and synthetic biology techniques. Tissue culture is currently an important way to solve the problem of drug sources. Given that the 代謝pathway of ginsenosides has gradually become clear, the expression of key enzyme 遺伝子can be increased through genetic 工学techniques to improve the synthesis of ginsenosides and obtain high-yield cell lines, thereby more effectively alleviating the growing demand for medicine and research and development. Biotransformation has outstanding advantages in obtaining rare ginsenosides and their aglycones, and it may also be possible to obtain ginsenoside derivatives that do not exist in natural plants. Synthetic biology research on ginsenosides is also a promising approach with broad development prospects.
ギンセノシドの生合成は、複数の要因によって制御される複雑で動的な過程である。を達成するためにginsenosidesという目標を合成生物学を通じて譲渡其ノ善後策ハ独リ旧態ヲがクローン関連鍵酵素を対象に適したシャシーの遺伝子細胞人為的遺伝子修正できるようにheterologous及び高効率な表情が投稿した深く鉱業を行うも規制ginsenoside代謝ネットワークを規範化する遺伝子、スイッチが見つかれが吹っ飛んだために代謝ネットワーク全体 これにより、代謝経路全体の遺伝子の全体的な発現レベルを改善し、より効果的にギンセノシドの生産を増加させる。これまでのところ、ギンセノシドの合成生物学研究は、生体成分の獲得や機能の検証という点で大きな進展が見られているが、シャシー細胞の修飾や代謝経路の構築に関する研究はまだ始まったばかりである。したがって、関連する分野が連携して本研究の発展を共同で推進すべきである。
参照
[1] 彼は DT、 王 B 陳 JM。 研究 progress 薬理作用に 効果 of ginsenosides [J]。J 遼寧前方面 Tradit あご Medです 2012年 14 . 118-121。
[2] 全羅南道木浦(チョンラナムド・モクポ)LP。 ginsenosides:化学,生合成,肛門-分解, and 潜在 健康 effects [J]。 Adv 食品 Nutr ^『官報』第56:1 -9。
[3] 佐 BM、 高 wxを乗算器115−xに、 洞 YY、 et アル 進歩 of the 薬用植物パナックス人参の組織培養[j]。 ^ a b c d e『仙台市史』、2012年、14 - 34頁。
[4] liu h, gao wy, zuo bm, etal。 panax quinquefolium l . [j]における組織培養の進展。 ^ a b c d e f g hi、2012年、14 - 14頁。
[5] gao wy, jia w, duan hq, etal。 薬用植物組織培養の工業化[j]。 ^ a b c d e f g h『仙台市史』、2003年、28 - 38頁。
[6] ウ KW, チョ wxを乗算器115−xに、 ハーン監督 EJ、 et アル ジャスモン 酸 チョウセンニンジンの不定根培養におけるギンセノシド蓄積を改善するc . a . meyer [j]。 ^ a b c d e f g h i j、2002年、211-215頁。
【7】 chen w, gao wy, jia w, etal。 専門は組織学、組織学 cell culture in medicinal 植物 人参の Lを有する。 [J]。 ^『仙台市史』仙台市史編纂委員会、2006年、166 - 166頁。
[8] 斗 ドラゴンクエスト、 金 L 陳 YJ。 進歩 and prospects 高麗人参の化学成分と薬理活性に関する研究[j]。 j . shenyang pharm univ ., 1999, 16: 151-156。
[9] -小橋K。 ギンセノシドの薬理作用に対する腸内細菌の関係[j]。 ^「biosci microflora, 1997」。biosci . 2016年4月1日閲覧。
[10] 長谷川 Hにする。 の証明 神秘的な 効能 人参:基本 and 臨床 裁判: metabolic 活性化 のginsenoside deglycosylation by 腸 細菌 and エステル化 脂肪酸で[j]。 j pharmacol sci, 2004年95: 153-157。
[11] 王 YZ、 陳 J 楚 SF、et アル 改善 记忆メカニズムに関する ネズミ and 増加 of 海馬の 興奮状態 in ネズミによって ginsenoside Rg1の metabolites ginsenoside Rh1 とprotopanaxatriol [J]。 ^ a b c d e f g h i j pharmacol sci, 2009, 109: 504-510。
[12] 柳 X, Dai JG。 進歩 in the 生体変換の研究 ginsenosides [J]。 人参 「Res publica、 2010年 22:修業。
[13] 張 YX、 陳 XY、 趙 WQ。 進歩 in studies biotransformation日 of ginsenosides [J]。 J 瀋陽 pharm univ ., 2008, 25: 419-422。
[14] wang y, liu th, wang w, etal。 変容に関する研究 ginsenoside Rg1 by 腸 植物 [J]。 中国 J ^ a b c d e f g h『仙台市史』、2006年、26 - 188頁。
【15位】 ペEA、チュッMK、朴EKはら ギンセノシドr (c)のヒトによる代謝 肠内细菌から and ◆ 関連 抗アレルギー活動[J]。 ^ a b c d e f g h『仙台市史』、昭和25年、743-747頁。
[16] ぺ・EAさんは漢MJ、チュッMK、ら 20(s)-および20(r)-ギンセノシドの代謝 Rg3 by 人間 腸 細菌 and in vitro生物活性との関係[j]。 2002年Biol Pharmブル、25:58-63。
〔17〕 ^ a b c d e f g h i j j j、j j j j j j j j j。 予備校-予備校 希少 ginsenosides biotransformationによって [J]。 ^『仙台市史』通史編、仙台市、2009年、676- 668頁。
[18] dong al, cui yj, guo hz, etal。 ギンセノシドの微生物学的変換 Rg1 [J]。 J あご Pharm Sci、 2001年 10: 114 - 118。
[19] Fu JG。 研究 on the 微生物 変換 of Ginsenoside[D] . 長春:吉林農業大学、2004年。
[20] チェンlqキム・マックリー・jw et アル 変換 ギンセノシド少佐のrb1です ginsenoside F2に caulobacter leidyia [j]著。^「biotechnol lett 2006年28: 1121-1127」。biotechnol lett(2006年). 2008年12月28日閲覧。
[21] bao hy, li l, zan lf, etal。 ギンセノシド再生物転換によって 中身はクモノスカビsp [J]。 Mycosystema、 2010年 29日:548-554。
。[22] 崔 Y 姜 BH、 韓 Y et アル 微生物 変換 ginsenoside 化合物 K から total saponins in 果物 高麗人参[j]です 2007年あごTradit薬草薬38:189-193。
[23] 柳 X, 巧 LR、 謝 D et アル 微生物 deglycosylationとketonization のginsenosides Rg1 and rb1 by fusarium oxysporum [j]。 j asian nat prod res, 2011年13: 652-658。
[24]大人 柳 X, 巧 LR、 謝D et アル 微生物 transformation ginsenosides-rg1のabsidia coeruleaによる代謝産物の多剤抵抗性腫瘍細胞への反転活性[j]。^『仙台市史』通史編1、通史編2、通史編2、1313-1317頁。
[25] 講 、SR choi kj, suzuki k, etal。 酵素準備 ギンセノシドのrg2、rh1、f1 [j]。 ^パウサニアス、2003年、51 -408頁。
[26] 講 、SR 鈴木 Y 鈴木 K et アル マーク production ギンセノシドrd、f2、rg3、および化合物kの酵素me- thodによる[j]。 ^『仙台市史』通史編、通史館、2007年、22- 27頁。
【27】 柳 L 朱 XM、王 プレイ、 et アル 酵素 準備 20 (Sの R) -protopanaxadiol by transformation 20 (Sの R) -Rg3 から 黒 ginseng [J]。 Phytochemistry、 2010年 71: 1514年)-永正17年(1520年)。
[28] liu l, gu lj, zhang dl, etal。 aspergillus nigerによる希少なginsenoside rfから20(s)-protopanaxatriolへの微生物変換[j]。 biosci biotechno1 biochem, 2010年74: 96-100。
[29] 金 DS」の 合図 ys, yu hs, etal。 Ginsenoside 酵素反応から調製したrh2 [j]。 ^ a b c d e f『仙台市史』通史館、2002年、21 -115頁。
[30] 能 ヘルプキーKH、 息子 晶文社 金 HJ、 et アル Ginsenoside 熱安定性be- ta-glycosidaseによる人参根抽出物からの化合物k産生 から Sulfolobus solfataricus [J]。 Biosci ^「bio1 biochem」。bio1 . biochem . 2009年3月23日閲覧。
[31] 柳 、モン Yeom SJ、 朴 CS et アル 生産 のaglycon protopanaxadiol曲輪K thermostable経由阝-glycosidaseから Pyrococcus furiosus [J]。 たら Microbiol 2011年Biotechnol、89:1019-1028。
[32] 陳 SL、 朱 XX 李 CF、 et アル ゲノミクス and 伝統的な中国医学の合成生物学[j]。 ^『仙台市史』通史編、仙台市、2012年、107 -107頁。
[33] 王 W 孟 C 朱 P et アル 予選 study 代謝日 engineering of 酵母 for 生産 taxadiene [J]。中国のバイオ技術、2005年、25:103-108。
[34] ajikumar pk, xiao wh, tyo ke, etal。 大腸菌におけるタキソール前駆体の過剰生産のためのイソプレノイド経路の最適化[j]。 科学、2010年、330:70-74。
[35] 香港 JQ、 王 W 王 LN、 et アル The 改善 酵母適合変異体によるアモルファ-4,11-ジエン産生の例[j]。^ a b c d e f g h『日本の歴史』、2009年、106 -951頁。
[36] Westfall -一体どう、 ピテラ DJ、 レニハン JR et アル 生産 抗マラリア剤アルテミシニンの前駆体であるジヒドロアルテミシニン酸への変換[j]。 2012年したNatl Acad Sci米国、109:E111-118。
〔37〕 呉 Q 周 YQ、 太陽 C et アル 進歩 in ギンセノシド生合成と二次代謝工学のための展望 the production of ginsenosides [J]。 中国 ^『日経産業新聞』2009年9月29日、102-108頁。
[38] 明 QL、 韓 T, 黄 F et アル 進歩 in studies ginsenoside日 生 and its 関連 enzymes [J]。 ^『仙台市史』通史編、仙台市、2010年、41 - 41頁。
[39] 呉 Q Sun C 陳 SL。 識別 and 3-ヒドロキシ-3-メチルグルタリル補酵素aレダクターゼ遺伝子の発現解析 from American ginseng [J]。 植物 」 J 2012年 5: 414-420。
[40] kim ot, bang kh, jung sj, et al。 人参ファルネシル二リン酸合成酵素遺伝子の分子特性とjasmonateメチルによるup- reg-の発現[j]。 ^パウサニアス、2010年、54 -53頁。
[41] アリ MB ウ KW, ハーン監督 EJ、 et a1。メチル jasmonate とsalicylic 酸 elicitaion を ginsenosides 蓄積酵素 and non-enzymatic α-リノレン in 中止文化 米国産人参」など根 in bioreactors [J]。 植物 ^アポロドーロス、2006年、25 -62頁。
[42] kim ot, kim sh, ohyama k, et al。 フィトステロールとのアップpregulation triterpene biosynthesis in ツボクサはasiatica毛むくじゃら 過剰発現したとき根 ginseng farnesyl リン酸 synthase [J]。^『人事興信録』第2版、人事興信録、2010年、403-411頁。
[43] 李 、モン 鄭 ジョナサン、 ソ 晶文社 et アル 拡張 パナックス人参のトリテルペンとフィトステロールの生合成過剰スクワレン synthase 遺伝子 [J]。 植物 セル Physiol、 2004, 45: 976-984。
[44] kim td, han jy, huh gh, et al。 発現と機能の特徴づけ 3 squalene synthase 遺伝子 関連付けられた ■サポニン生 in panax高麗人参[j]。 植物 2011年セルPhysiol、52:125-137。
[45] ソ・ジョウシン・cg他1 eleutherococcus senticosusにおけるスクア-レン合成酵素の過剰発現は、植物-テロルおよびトリテルペンの蓄積を増加させる [J]。 ^ a b cアポロドーロス、2005年、66 - 86頁。
[46] 姜 SC 張 ぐらい、 王 Y et アル 干渉 高麗人参のsqs遺伝子のベクター構築と形質転換カルス [J]。J 吉林 Univisity、 2011, 49: 1136-1140。
[47] 韓 嬢王、 In JG、 権 金泳三(キム・ヨンサム et アル 規制 rnaインターフェレンスによるギンセノシドおよびフィトステロール生合成について[j]。 ^アポロドーロス、2010年、71 - 36頁。
[47] 姜 SC 柳 WC、 王 Y et アル 相関 ギンセノシドの蓄積とsqsおよびsqe遺伝子発現の間に存在する 異なる 機関 パナックス・クインケフォリウス[j]です あご ^『仙台市史』通史編、仙台市、2011年、579-584頁。
[49] 釧路 T, 大野 Y 渋谷 M et a1。 in vitroでの2,3-oxidosqualeneからdammarenediolへのパナックス人参ミクロソームによる変換[j]。 ^『仙台市史』通史編、通史編、292-294頁。
[50] tansakul p, shibuya m,钏路t, et al。 Dammarenediol-II ギンセノシド生合成のための最初の専用酵素であるシンターゼ[j]。2006年それLett fbi、580:5143-5149。
[51] 韓 嬢王、 権 金泳三(キム・ヨンサム ヤン DC et al. 表情 and rna干渉によって誘発されるdammarenediol synthase遺伝子のサイレンシング in 米国産人参[J]。植物 セル Physiol、 2006, 47: 1653-1662
[52] lee mh, han jy, kim hj, et al。 ダムマレネジオールiiの生産は、パナックス人参ダムマレネジオールiiを発現するトランスジェニータバコにtmv耐性を与える synthase [J]。 Plant cell ^パウサニアス、2011年、53 - 173頁。
[53] 釧路 T, 渋谷 M Ebizuka Y "はない 阝-Amyrin 高等植物で最も一般的なトリテルペンの形成を触媒するオキシドスクレンシクラーゼの合成酵素クローニング[j]。 ^ a b c d e f g h『日本の歴史』、1998年、256:238-244頁。
[54] zhao sj, hou cx, liang yl, et al。 クローンの高丽人参阝w遺伝子 and the 建設 of its antisense 植物 表情ベクトル [J]。 China Biotechnol、 2008年28:74-77。
[55] 牛 YY、 羅 うん 黄 LF。 進歩 in the study cyp450のギンセノシド生合成に関与する[j]。 世界Sci ^『仙台市史』仙台市史編纂委員会編、仙台市史編纂委員会、2012年、117 - 117頁。
[56] 韓 嬢王、 Kim HJ、 権 金泳三(キム・ヨンサム et al. The Cyt P450 酵素cyp716a47は、ダムマレネジオール- iiからプロトパナキサジオールを形成する 中 ginsenoside biosynthesis in 米国産人参[J]。 plant cell physiol, 2011, 52: 2062-2073。
[57] 陳 SL、 羅 うん 李 Y et アル454 」EST 分析 panax高麗人参のギンセノシド生合成に関与すると推定される遺伝子を検出[j]。 ^『人事興信録』人事興信録第30号、人事興信録第30号、1593- 1561頁。
[58] sun c, li y, wu q, et al。 De管理者 gs flxチタンを用いた米国人参根トランスクリプトームの塩基配列解読と分析 プラットフォーム to 発見 putative genes involved in ginsenoside biosynthesis [J]。BMCGenomics、 2010, 11:
262-273。
[59] luo hm, sun c, sun yz, et al。 高麗人参の根のトランスクリプトームを解析すると、トリテルペンサポニンと推定される生合成遺伝子と遺伝子マーカーが明らかになった[j]。 ^ a b cアポロドーロス、2011年、12頁。
[60]韓 嬢王、 黄 HS、 崔 SW、 et al. シトクロム P450 CYP716A53v2 同時に皮膚 the formation of protopanaxatriol protopanaxadiolから 中 ginsenoside生 in pa - nax ginseng [j]。 ^「plant cell physiol, 2012, 53: 1535-1545」(英語). plant cell physiol . 2012年5月15日閲覧。
[61] chen x, xue y, liu jh, et al。 パナックス人参毛根培養からのグルコシルトランスフェラーゼの精製と特性評価[j]。 ^『仙台市史』仙台市、2009年、16 - 50頁。
[62] 略称はjj、jj。 udpgの精製と特性評価:ginsenoside Rd glucosyltransferase from 中断 細胞 of 叶サポニンス・[J]。 2005年した生化学、40:3742 -
3748.


 英語
英語 フランス
フランス スペイン
スペイン ロシア
ロシア 韓国
韓国 日本
日本




