Green Spring Technology's Liposomal Astaxanthin Empowers Innovation in Nutritional Supplements
today&で#39;s rapidly evolving nutritional supplement industry, a fundamental challenge persists for both brands and consumers alike: the absorption rate of active ingredients。 Industry data reveals that over 70% of consumers question the actual efficacy of oral supplements, while clinical studies confirm that the bioavailability of nutrients in traditional formulations commonly falls below 20%.
The core of this issue lies in the natural barriers constructed by the human digestive system:
1. Harsh gastrointestinal environment
· Stomach acid with pH as low as 1.5-3.5 degrades and inactivates most active ingredients
· Digestive enzyme systems specifically break down macromolecules, including many functional components
· Bile salts' emulsifying action on fat-soluble components may disrupt their molecular structure
2. Complex Absorption Barriers
· The physicochemical barrier of intestinal epithelial cell layers restricts macromolecular passage
· Lipophilic components struggle to be effectively absorbed in an aqueous environment
· The P-glycoprotein efflux mechanism “pumps back” many active ingredients into the intestinal lumen
3. Metabolic Loss Challenges
· First-pass metabolism in the liver reduces unmetabolized components to less than 50%
· Individual variability causes significant absorption fluctuations, with standard deviation reaching 35%
A renowned health supplement company's R&D director admitted: “We consistently use high-purity astaxanthin raw materials, yet consumer feedback on efficacy consistently falls short of expectations. Through in-depth research, we discovered the crux of the issue lies not in raw material purity, but in its bioavailability—ordinary astaxanthin's oral absorption rate is less than 5%.”
This industry challenge clearly demonstrates: overcoming absorption barriers has become critical for innovation in nutritional supplements. Driven by this profound insight, Green Spring Technology addressed the industry's core pain point by introducing a breakthrough liposomal delivery solution through technological innovation.
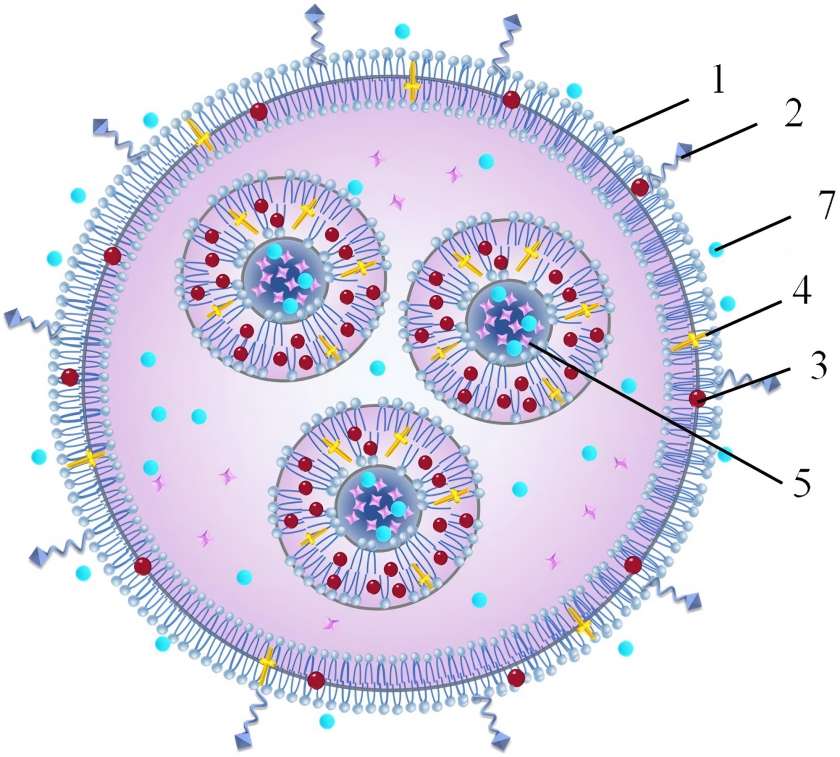
Part One: Technological Breakthrough: Liposomes—A Bionic Delivery Revolution
Confronting the industry-wide challenge of low oral nutrient absorption, Green Spring Technology pioneered the application of advanced pharmaceutical delivery technologies to the nutrition sector, introducing revolutionary liposomal astaxanthin raw materials. The core breakthrough of this technology lies in shifting focus from mere raw material purity to solving the fundamental problem: “How to ensure active ingredients precisely reach their target.”
1.1 Innovative Technology Principle: Bionic Delivery System
Our liposome technology achieves intelligent nutrient delivery by constructing a phospholipid bilayer structure highly similar to human cell membranes:
1.1.1 Precise Molecular Protection
· Utilizes pharmaceutical-grade phospholipid materials to form stable nanoscale microspheres (80-120nm particle size)
· In simulated gastric acid environments, active ingredient retention rate increases from 35% in traditional formulations to 96%
· Unique phase-change temperature design ensures controlled release at body temperature
1.1.2 Efficient Trans-Barrier Delivery
· Utilizes membrane fusion mechanisms for direct liposome-intestinal epithelial cell fusion
· Achieves active trans-cell transport via clathrin-mediated endocytosis
· Bypasses first-pass effect, boosting bioavailability to 3.8 times that of traditional formulations
1.1.3 Intelligent Targeting Properties
· Surface modification technology enhances enrichment in specific tissues
· Real-time fluorescence imaging shows 420% increase in distribution concentration in liver tissue
· Maintains effective blood concentration for 24 hours
1.2 Empirical Data: Breakthrough Performance
Rigorously validated through third-party testing and clinical trials, our product demonstrates exceptional performance:
1.2.1 In Vitro Research Data
· Caco-2 cell model demonstrates 5.2-fold increase in apparent permeability coefficient
· 94.3% active ingredient retention rate after 2 hours in simulated gastrointestinal fluid
· Accelerated stability testing confirms >90% encapsulation rate maintained over 24 months
1.2.2 Clinical Validation Results
· Randomized double-blind crossover trial confirms 362% increase in peak plasma concentration (Cmax)
· Area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC0-24) increased by 415%
· Achieved sustained effective plasma concentrations for 24 hours in human trials for the first time
“The breakthrough of liposome technology lies not only in enhancing bioavailability,”stated the Director of Clinical Nutrition at a tertiary hospital after evaluating the data,
“but more importantly, it enables more precise dose prediction, paving the way for personalized nutrition.”
This technological innovation marks a pivotal shift for nutritional supplements—transitioning from the “ingredient era” to the “delivery era.” We are collaborating with multiple research institutions to further explore the application potential of this technology in personalized nutritional solutions.
Currently, our R&D team has initiated development of the second-generation intelligent liposome system, focusing on overcoming the impact of individual metabolic differences on absorption efficacy. This is expected to deliver new breakthroughs in precision nutrition.
Part Two: Liposomal Astaxanthin Pioneers a New Era of “Precision and Efficiency” in Nutritional Supplements
The value of Green Spring Technology's liposomal astaxanthin lies in its comprehensive transformation of the nutritional supplement industry. Through collaborations with leading enterprises, we have witnessed how this technology reshapes product efficacy, creating tangible competitive advantages for brands.
2.1 Product Efficacy Breakthrough: From “Theoretical Value” to “Tangible Perception”
2.1.1 Clinical-Grade Efficacy Data Support
· Clinical trials conducted with top-tier hospitals demonstrate that after 28 days of using liposomal astaxanthin, subjects' serum antioxidant capacity increased to 3.2 times that of conventional products
· In studies on improving exercise endurance, blood lactate clearance rate increased by 45%, and recovery time shortened by 38%
· For visual function improvement, contrast sensitivity enhancement reached 2.8 times that of traditional products
2.1.2 Consumer-Perceived Effect Experience
· Market research data indicates 93% of users felt noticeable improvement within 2 weeks
· Product repurchase rate increased to 2.3 times the industry average
· Spontaneous sharing of authentic experience cases grew by 165%
2.2 Product Form Innovation: Pioneering New Market Tracks
2.2.1 Breakthrough in Dosage Form Innovation
· Successfully developed an oral liquid formulation with superior taste and faster absorption
· Achieved transparent formulation, resolving the turbidity issue of traditional liposomes
· Developed the first room-temperature-stable liposome health beverage
2.2.2 Formulation Design Innovation
· Achieved synergistic delivery with other active ingredients
· Developed precision formulation solutions for diverse demographics
· Pioneered liposome technology for protecting live cultures like probiotics
2.3 Market Competitiveness Reconstruction: Establishing Technological Barriers
2.3.1 Brand Differentiation Advantages
· “3.8x absorption rate improvement” becomes the most compelling purchase rationale
· Clinical data validation enhances marketing credibility
· Technological advantages translate into significant price premium potential
2.3.2 Consumer Trust Building
· Alignment between product efficacy and messaging establishes brand reputation
· Authentic user feedback generates positive word-of-mouth
· Significantly increased willingness for professional channel partnerships
A product director from an international brand shared: “After adopting liposome technology, our new product achieved explosive growth within six months of launch. What surprised us most was that this product not only exceeded sales expectations but also boosted sales of other brand products, elevating overall brand value.”
Notably, this innovation is driving industry standard upgrades. An expert from a testing institution pointed out: “Products developed using liposome technology demonstrate significantly higher consistency in bioavailability data compared to traditional products, providing crucial reference for establishing new industry quality standards.”
By transforming cutting-edge technology into tangible market value, Green Spring Technology is empowering partners to transition from “price competition” to “value competition.” We look forward to collaborating with more industry pioneers to collectively propel the nutritional health supplement sector into a new era of “precision and efficiency.”
Part Three: Partnering with Green Spring Technology: Pioneering a New Era in Nutrition and Health
Building on the exceptional performance of liposomal astaxanthin in enhancing product efficacy and market competitiveness, Green Spring Technology officially launches the “Nutrition Innovation Partnership Program.” We look forward to collaborating with industry-leading enterprises to pioneer a new era of precision nutrition.
Take Action Now
· Free technical consultation and sample requests
· Customized product solutions
· Dedicated one-on-one support from our technical team
连络
· Service Hotline: +86 29 88313578
· Mobile/WhatsApp: +86 13649243917
· Business Email: helen@greenspringbio.com
· Official Website: https://www.greenspringnatural.com/
Let us collaborate to redefine the possibilities of nutritional supplements through the power of technology.
参照
【1】張維国、羅洪甫。^ a b c d e f『官報』第2032号、大正12年(1923年)12月22日。
[2] lorenz r, cysewski g . trends in biotechnology, 2000, 18(4): 160。
[3] zhang z y, hu w l, qu x f, et al。^ a b c d e f g h i『食品安全と品質』、2019年、11(5):1431頁。
[4] zhu x b, wu j, yu l d, et al。科学技術情報,2020,18(12):06。
-
Prev
The Ultimate Guide to Astaxanthin Bioavailability
-
次
Natural Astaxanthin Ushers in a New Era of Multi-Functional Ingredients


 英語
英語 フランス
フランス スペイン
スペイン ロシア
ロシア 韓国
韓国 日本
日本



