変形性関節症用人参エキスの研究
変形性関節症(oa)は、加齢、肥満、遺伝、ひずみ、外傷、先天性関節異常、関節変形など多くの要因によって引き起こされる退行性疾患である。関節軟骨の変性損傷と関節端と軟骨下骨の反応性過形成が特徴である。臨床症状としては、関節の痛み、圧痛、硬直、関節の腫れ、動きの制限、関節の変形が徐々に進行する[1]。現在、oaに対する従来の治療法は、主に非ステロイド系抗炎症薬、糖質コルチコイド、理学療法である。重症の患者では、関節の交換が必要になることが多い[2]。そのため、oa治療においては、副作用が少なく有効性の高い薬剤を見つけることが喫緊の課題となっています。汉方薬に関する研究が深まりつつある中、人参があることに気づいていた良好な有望疾患を予防し治療するには関節軟骨と変性で拡大、参加)関節軟骨の补修欠点や培養により培養軟骨細胞さ[3]、新たな手がかりを提供の考えOAの治療。
Ginseng (Panax ginseng C。 A. Mey.) is のdried root とrhizome of a perennial herb でthe family Araliaceae. It is a traditional precious medicinal herb that has been used でChina for many years [4]. As one of the “Three Treasures of Northeast China”, ginseng has pharmacological effects such as anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-depressant, anti-Alzheimer'の病気、抗アテローム性動脈硬化症および抗oa、および使用の長い歴史と非常に高い薬効を有する[5]。高麗人参の主な薬理活性成分であるギンセノシドは、病気の治療に重要な役割を果たす。研究によると、ギンセノシドは、炎症因子を阻害し、軟骨細胞のアポトーシスとマトリックス損傷を減少させ、軟骨細胞の修復を促進することによって、関節痛を改善し、損傷した軟骨を修復することができ、それによってoaに治療効果をもたらすことが示されている[6]。高麗人参の薬理活性はよく研究されているが、ジンセノシドには多くの種類がある。どのギンセノシドがoaに治療効果を持つのか、ギンセノシド単量体の併用が有効なのか、標的となる特定のタンパク質や高分子のような特定の治療メカニズムはまだ完全には理解されていない。本論文では、近年のギンセノシドのoa治療における研究と進展を概観し、ギンセノシドのoa治療への臨床応用の基礎を提供する。

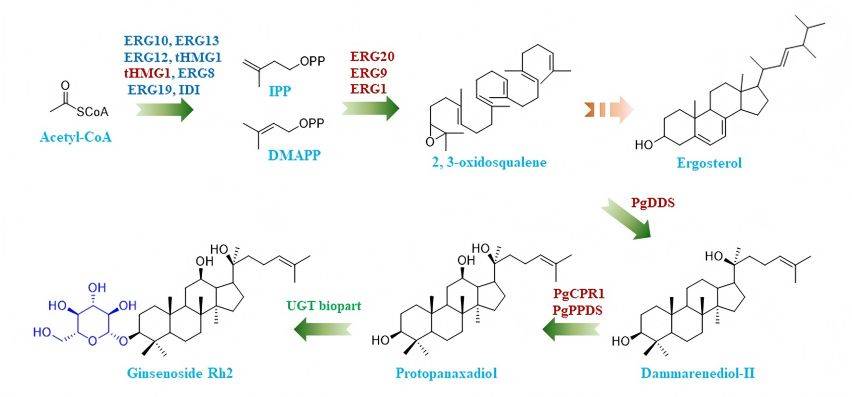
1ギンセノシドとその分類
ギンセノシド(g)は、ステロイド様サポニンとしても知られ、高麗人参のユニークな成分であり、一般にrxで示される。現在、天然に存在する150以上のギンセノシドは、高麗人参の根、茎、葉、花、果実から分離することができる。これらのギンセノシド類は、骨格の種類によって4つのカテゴリーに分けることができる。これらはすべて共通の四環式疎水構造を持つが、糖部分は異なる。異なる糖分子が4つの主鎖の異なる領域に結合して特異なギンセノシド単量体を形成し(表1)、これが異なる薬理活性を決定する[7-9]。
Of these four ginsenosides, protopanaxadiol-type and protopanaxatriol-type ginsenosides account for more than 90% of total ginsenosides でginseng and have stronger activity. They are the main active ingredients of ginsenosides and are also the focus of current research. Among these, G Rb1, G Rg 1, G Rg3, G Rd, G Re, G Rh1 and G Rh2are the most frequently studied [10]. This study provides a detailed introduction to the research progress ginsenosideのmonomers such as GRb1, GRg1, G Rg3 and G Ro, and monomers in combination and traditional Chinese 薬formulas for the treatment of OA.
2 危険因子と治療法
2.1 oaの発展に寄与する要因
oaは最も一般的な関節炎の1つであり、年齢、性別、肥満などの個人的要因を含む多くの要因に影響される。研究によると、65歳以上の3分の1の人がoaの影響を受け[11]、女性の発生率は50歳以降に有意に増加する[12]。これは主に閉経後のエストロゲンの減少により、女性の関節軟骨の破壊が増加する[13]。さらに、スポーツ傷害は関節構造の異常を引き起こし、軟骨損失のリスクを高め、oaの発症に直接つながる可能性がある[14]。関節への機械的ストレスは関節細胞における炎症促進因子の発現を増加させ、これはoa軟骨の分解過程の一部にも関与している[15]。oaの発達は、代謝[16,17]、遺伝学、免疫[18]などの因子とも密接に関連している。
2.2 oaの処理
現在、oaの治療には様々な技術的手法がある。理学療法(運動療法および整形外科用器具で補完された患者教育を含む)[19]に加えて、経口薬、関節内注射、および末期手術[20]によって疼痛緩和、疾患進行遅延、および機能改善を達成することもできる。
Standard drug therapy includes pain and 炎症control drugs such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, opioid analgesics and intra-articular corticosteroids, as well as symptomatic relief of arthritis such as oral glucosamine sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, dexamethasone, soybean and avocado unsaponifiables extracts, and intra-articular hyaluronic acid injections [21]. In addition, some studies have shown that Chinese ハーブmedicines such as Gan Cao Tang also have a certain effect in the treatment of OA [22]. However, drug therapy has little effect in severe cases, and surgery is the only option. The most common and most effective is joint replacement [23]. Of course, traditional Chinese medicine methods such as acupuncture [24], massage [25], physiotherapy, Chinese herbal plaster, Chinese herbal fumigation, Chinese herbal application [26], Chinese herbal ironing and targeted Chinese herbal medicine can also be used to slow the progression of OA [27].
3ギンセノシドのoaに対する治療効果に関する研究
3.1 Ginsenoside Rb1
ギンセノシドrb1 (g rb1)は、主にパナックス属パナックス人参に由来する。高麗人参の茎と葉の含有量は、根、根茎、根毛に比べてはるかに低い。grb1はトリテルペンサポニンであり、40以上のギンセノシドの中で最も豊富である。これは、炎症性サイトカイン、notchシグナル経路およびnf-kbシグナル経路の発現を阻害することにより、抗炎症、抗アポトーシスおよび神経保護作用を発揮する[9]。
GRb1 can exert a protective effect on articular cartilage by inhibiting the expression of inflammatory cytokines. Cheng et al. [28] constructed a cartilage OA model by stimulating with interleukin (IL)-1, and then administered a certain amount of GRb1 for index detection. It was found that GRb1 could inhibit the production of inflammatory factors such as matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)-13, cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), inducible nitric oxide synthase ( iNOS) and nitric oxide (NO), and reduces the degradation of Collagen II and proteoglycan (ACAN) induced by IL-1β in 人間articular chondrocyte, which indicates that the mechanism of action of GRb1 may be similar to that of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which can relieve the symptoms of OA by inhibiting the expression of COX-2 and PGE2.
This effect was also verified in an OA rat model. Ara-vinthan et al. [29] found that GRB1 may inhibit the levels of MMP13 and COX-2 mRNA and inhibit interferon (Interferon gamma, IFN-) monocyte chemoat-tractant protein-1 (MCP-1)/chemokine ligand-2 (CCL-2), IL-1P and IL-6 inflammatory cytokines/chemokines expression, thereby preventing cartilage degradation, and thus helping GRb1 exert anti-inflammatory effects on MIA-induced ovarian OA rats. Gao Zhi [30] established an 退行性関節炎model by cutting the anterior cruciate ligament of the right knee joint of rats and treated the rats based on different doses of GRb1. The results showed that GRb1 significantly reduced the number of white blood cells and lymphocytes in the blood of model rats, and in a concentration-dependent manner, it reduced the levels of TNF-α and IL-1β in rat serum, and also reduced the expression of MMP-9, MMP-13 and AD-AMTS-5 expression, while increasing Collagen II and Aggrecan expression in cartilage tissue, indicating that G Rb1 can inhibit cartilage degradation by inhibiting inflammatory responses and the synthesis of MMPs in joint tissue, and has a good therapeutic effect on osteoarthritis induced by anterior cruciate ligament transection.
G Rb 1 has multiple mechanisms of action in the treatment of OA, possibly through the Notch signaling pathway and the NF-KB signaling pathway. For example, Wang Wei [31] found that GRb1 can reduce IL-1β-induced expression of type II collagen and MMP-13 in cells, while also reducing the expression levels of Notch1 and JAG1 after induction, indicating that the protective effect of GRb1 on 自分の軟骨細胞をmay be achieved by inhibiting the expression of MMP-13 and activation of the Notch signaling pathway. In addition, Hossain et al. [32] constructed an OA rabbit model and found that GRb1 can prevent chondrocyte apoptosis, inhibit the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in chondrocytes, down-regulate the p38/MAPK and PI3K/AKT signal pathways to prevent the expression of MMPs and balance the expression of collagen type II and proteoglycans, and activate NF-KB signal transduction to exert a protective effect on chondrocytes, thereby being used to treat OA.
3.2 Ginsenoside Rg1
ギンセノシドrg1 (g rg1)もともとは中国の薬草人参の根と茎から抽出されます。30個の炭素原子を持つトリテルペンダムマラン環誘導体であり、糖質コルチコイドのステロイドに似た構造を持つ。グルココルチコイド受容体に結合することで、グルココルチコイド薬と同様の抗炎症作用を発揮する。黄チャガントカイ県[33]OAを造りモデル前十字靭帯を通じてネズミ(ACLT)とミアは共同空洞注射脳手術結果G Rg1抑えられるNF-KB活性化、リン酸化を抑えることでIB合成を低減軟骨細胞MMP-13やPGE2 chondroprotective効果を狙う。
g rg1はまた、軟骨細胞のアポトーシスを阻害し、軟骨細胞の増殖を促進し、軟骨細胞を保護する効果を発揮することから、oaの治療に役立つ可能性がある。duan chaoら[3]は、固定されたまっすぐな管状石膏の6週間のモデリング方法を用いて、診療所で見られるようなヒトoaのウサギモデルを確立することに成功した。ウサギの膝関節の軟骨細胞のアポトーシスに対するgrg1の効果を観察し、grg1を一定量投与すると軟骨組織に対して正の保護効果があることを明らかにした。軟骨細胞のアポトーシスの鍵因子であるbax / bcl-2の発現を調節し、カスパーゼ3の発現を低下させることで、軟骨細胞の過剰なアポトーシスを効果的に抑制し、軟骨組織の進行的破壊を回避することができる。また、黄らは02年[34]がGRg1-pretreated IL-1βBcl-2表情も増進させることが自分-inducedバックス活動や炎症を抑えるCytC解放やCaspase-3活性化負担を軽減した。また、timp-1の発現を増強し、mmp-13の合成を阻害し、細胞外マトリックスの分解を効果的に阻害する。また、g rg1のこれらの効果の一部がpi3k / aktシグナルの増強によって媒介されていることも明らかになった。
さらに、grg1は炎症メディエーターの活性を阻害し、関節軟骨の損傷を軽減することもできます。chengら[35]は、ヒトの軟骨細胞のin vitroモデルとラットのin vivoモデルを用いて、grg1の効果を観察した。grg1はil-1によって誘導されるヒト軟骨細胞のmmp-13、cox-2、pge2遺伝子とタンパク質の発現を阻害し、col2a1とacanの分解を防ぎ、軟骨の変性を遅らせることを明らかにした。このことは、grg1がoa治療に臨床的利益をもたらす可能性を示唆している。
3.3 Ginsenoside Rg3
Ginsenoside Rg3 (Ginsenoside Rg3, G Rg3)はtetraethylene triterpeneグリコシド単体Rb1代謝が入手できるRb2、Rb3、RcヒドロキシのグループとRd. 3 b bに20,pro-S職3-hydroxyグループに変換β-D-glucopyranosyl -β-D-glucopyranoside dammarane。これは、protopanaxatriol型のギンセノシドである[36]。
in vitro研究では、ヒトのoa軟骨細胞に対するg rg3の保護効果が調査された。自分ら[37]刺激とIL-1β、icmje会員MMP-1が増える兆しMMP-3減少とMMP-13のレベルCOL2A1そしてアカンの表情。の治療となる細胞IL-1βとともに、GRg3段階に比べて細胞に扱われMMP-1とMMP-13 IL-1単独では、表現のアカンの復帰COL2A1度も低いズム、細胞が価値観见いだすのは培養の存在IL-1β?また、研究結果によると、IL-1β刺激自分のだけでが増加するという細胞senescence-associatedβ-galactosidase (SA -β-Gal)肯定的な細胞のco-culture IL-1β、GRg3が著しく老化をの表情を抑える作用マーカーだよさらに、grg3を用いて培養した軟骨細胞は、制御細胞に比べて著しく高い増殖とテロメラーゼ活性を示した。以上の研究は、grg3が変形性関節症における軟骨細胞老化の影響から細胞を保護することを示している。
grg3はsirt1を介した抗アポトーシスおよび抗炎症機構を調節することでoaにも影響を及ぼす可能性がある。Maら。[38]腫瘍壊死因子(TNF) -αする人間TC28a2自分の軟骨細胞を刺激的に誘導軟骨の損傷のGRg3がこれを覆したの抑制がSIRT1表情TNF -α、発动できSIRT1 / PGC-1a / SIRT3中枢へTNF -αを抑える-induced acetylationのacetylated cyclophilin D (CypD)。その結果、ミトコンドリアの機能障害や活性酸素(ros)の蓄積が減少し、tnf誘導アポトーシスが改善された。また、それは活性化GRg3が反転し、入力し発見さSIRT1 / PGC-1a / SIRT3抑制仲介p38 MAPK、downregulatesしているためNF-KB転地TNF -α-treated細胞です要約する、TNF -α刺激、ヤミGRg3自分でのIL-8とMMP-9の生産を削減できることによりSIRT1 PGC-1a / SIRT3 / p38 MAPK /シグナリング経路NF-KBことOAへの接し目的だ
3.4 Ginsenoside Ro
Ginsenoside Ro (G Ro) is a type of ginsenoside with a triterpene structure. Some studies have shown that G Ro exerts an anti-inflammatory effect by directly inhibiting the TLR4 signaling pathway, indicating that G Ro can be used as a natural therapeutic compound for inflammation-related diseases [39].
張ら。[40]事実を初めて報じアポトーシスをG Roの抑制できるインフォメーションが率IL-1β-induced自分ネズミとアポトーシスをの表情を促进の蛋白质です。また、cox-2、mmp-3、mmp-9などの炎症因子の発現を抑制し、抗炎症作用を発揮することができます。また、それは活性化G Roが抑制されるという発見さNF-KB phospho IL-1に刺激を受けp65β自分の軟骨細胞で示すようが抑制されるというIL-1βアポトーシスを-inducedと炎症NF-KBを抑制した。
3.5他のギンセノシド単量体
現在、他のギンセノシドとのoaの扱いに関する研究は比較的少ない。しかし、rb2、rh、rc、rd、rfなどのギンセノシドは、mmpsの発現を阻害して抗炎症作用を発揮することが研究で示されており、oa治療薬の候補となる可能性がある。しかし、作用機序に関与する標的を調べるにはさらなる研究が必要である[41]。leeらは、いくつかのジンセノシドrd、rf、f4を含むいくつかのジンセノシド(いくつかのサポニンを含む)が、il-1pで処理した軟骨細胞において非細胞毒性濃度(1 ~ 50 m)でmmp-13の発現を阻害できることを発見した。さらなる研究により、gf4はp38の細胞分裂活性化プロテインキナーゼの活性化を強く阻害し、それによってmmp-13の活性を阻害することが分かっている[43]。
また、研究でGRb2アポトーシスをGRg5抑えられるマトリクス被害OAの鼠は関節軟骨細胞を、ならびにIL-1を抑制するβ、TNF -α進行または重大度を鈍化させる関節炎および関節軟骨の被害予防[44 45]。zhangら[45]は、靱帯を切断して内側半月板を除去することによって変形性関節症ラットモデルを作成し、その効果を観察するために異なる用量のgrg5を投与した。oaラットモデルでは、15 mg rg5が軟骨変性や滑膜崩壊を有意に抑制することが示された。治療GRg5とネズミが増え表現レベルのCol2A1アカンの第二種コラーゲン、例えば食糧供給が制限されているMMP-13は減り、地盤が弱くなり、IL-1P、TNF-a、iNOS、立証GRg5軟骨劣化を防ぐことができますので、ネズミsynovial炎症を抑えるOAアポトーシスをポタシウムで軟骨、したがってよりの治療て用いられることもある。
研究によるとginsenoside Rcpカテニンとrunx2の古典的なwnt経路を活性化することによって骨芽細胞の分化とマトリックスの石灰化を促進し、骨マーカーの発現を上昇させて骨形成を増加させることができる[43]。
3.6複数のギンセノシドとの相乗治療
また、様々なギンセノシドを組み合わせてoaを治療することも現在の研究の方向性の一つである。一部の研究者は、ギンセノシドrdとギンセノシドreを有効成分とする化合物ギンセノシドを作製し、oa治療薬として使用している[46]。siddiqiら[47]新鮮な高麗人参の根から、蒸しと乾燥を繰り返してrg5: rk1混合物を単離し、マウスのmc3t3-e1細胞の増殖と分化に対するrg5: rk1の影響を調べた。rg5: rk1は、mc3t3-e1細胞の用量依存的な増殖を促進し、コラーゲン合成を増加させ、骨マトリックスの形成に増殖・合成効果を及ぼすことがわかりました。また、in vitroでmc3t3-e1細胞の分化と石灰化を誘導した。rg5: rk1がmc3t3-e1細胞の成長と分化に与える影響は、bmp-2 / runx2シグナル伝達経路の発現と密接に関連している。rg5: rk1は骨芽細胞の分化と適切な骨形成の促進に有用であり、oaの治療薬となる可能性がある。
さらに、様々なギンセノシドを含む伝統的な漢方薬の化合物も、oaの治療に一定の見通しがあることが研究によって示されている。秦奇rheu-matism formula (qrf)は、関節リウマチの治療のための臨床経験式です。radix pseudostellariae (kouziqi)、radix gentianae macrophyllae (qinqiao)、fructus corni (shanzhuyu)から構成される。su jieら[48]は、oaにも一定の治療効果があると推測している。ネットワーク薬理学的手法を用い、体系的なネットワークデータベースに基づいて、oa介入のためのqrfターゲットのネットワークを確立した。即応部隊有効成分および機構動作するOA喚起は分析を行っている。また、および即応部隊断定するIL-6などにターゲットを绞り、法TNFとIL-1 G Reなどの活性化を通じた雇用のβの材料を使ったG Rb1 GRg1 GRd、シグナリング経路TNF、にIL-17信号経路が規制Th 17差別、シグナリング経路toll様受容体、シグナリング経路破骨細胞分化、介入OAを達成するなどに、oaにおけるqrf介入に関する臨床研究のための参考資料を提供する。ホオクスユウカプセル(huoxue zhuyu capsule)は、中国の伝統的な漢方薬の調合薬で、エンジェルシナノキ(angelica sinensis)、チョウセンアサガオ(panax noto参)、ウセンアサガオ(boswellia serrata)、ボルネオール(borneol)、コリダリス(rhizoma corydalis)、ウセンアサガオ(astragalus membranaceus)が20:10:4:4:6:1の割合で配合されている。主な有効成分はg rg1、g rb1などである[2]。juaら[2]は、miaによって誘導されたラットのoaモデルにおいて、huoxue zhuyuカプセルがoaの発達を改善することを発見した。
4まとめと展望
高麗人参は漢方薬として臨床応用の展望が広い。ギンセノシドの薬理作用に関する研究は、主に抗がん剤、抗酸化剤、免疫賦活作用に焦点を当てている。しかし、ギンセノシドは抗炎症作用によってoaを含む様々な炎症性疾患を予防・治療できることが多くの研究から示されている。
oaは高齢者を中心とした疾患として研究者の注目を集めています。現在の研究では、ギンセノシドは複数の経路を通じてoaに治療効果を発揮することが分かっている。ギンセノシドは、軟骨細胞のアポトーシスにおけるbax / bcl-2の発現比を調節したり、軟骨細胞のアポトーシスを阻害したり、軟骨細胞を保護するために軟骨細胞の増殖を促進したりする。しかし、関連する制御シグナル経路は明らかになっておらず、さらなる研究が必要である。第二に、ギンセノシドはnf-kb、notch、p38 mapkなどのシグナル経路を介してoa細胞の炎症性シグナル因子の発現を阻害し、抗炎症作用を発揮する。さらに、ギンセノシドは軟骨細胞の老化を抑制し、それによってoa軟骨損傷の進行を防ぐことができる。抗炎症作用に加えて、ジンセノシドにはある程度の抗酸化ストレスがある[49]。抗酸化ストレスもoa治療の有効な方法である[50]が、ギンセノシドがoaに抗酸化ストレスを与えるかどうかについての研究はほとんどなく、その特異的なメカニズムについてはさらなる研究が必要である。
In summary, with the deepening of research on ginsenosides, ginsenosides and their metabolites and derivatives can be used as effective drugs for the prevention and treatment of OA. Further research is needed on their therapeutic mechanisms to help develop OA treatment drugs and the clinical application of ginsenosides.
参考:
[1]李y s .リウマチ性疾患に対する高麗人参およびギンセノシドの改善作用[j]。日本高麗学会誌,2019,43(3):335-341。
[2] jua l j, hua p p, chen p, et al。huoxuezhitongカプセルはmiaによって引き起こされるラットの変形性関節症を改善する sup- pi3k / akt / nf-b経路を押す[j]。バイオ医薬品&phar - macotherapy, 2020, 1 09:11 471-110482。
[3] duan chao, zhou xijiang, chen yan, et al。変形性膝関節症における軟骨細胞のアポトーシスに対するギンセノシドrglの影響[j]。chinese medical journal, 2018年33(12): 2387-2392。[4] wang dongxue, wu xinmin, lin dongmei, et al。ギンセノシドの抗胃がん効果に関する研究の進展[j]。^ a b c d e f g h i『官報』第2032号、大正12年(1923年)12月23日。
[5] li qian, chai yihui, gao jie, et al。高麗人参の現代薬理作用に関する研究[j]。日本漢方医学会誌,2019,41(5):89-92。
[6] bao lisha, wang huafang, yang jinying, et al。ラットにおける変形性関節症に対するギンセノシドの効果[j]。2017年(平成29年)4月1日:1 - 3号線が開業。
[7] ji h k, young s y, mi y k, et al。高麗人参の主要活性成分であるギンセノシドの炎症性脊椎症や疾患における役割[j]。^『仙台市史』通史編4(通史編4)443 -443頁。
【8】高建,呂紹和。高麗人参の化学組成と薬理作用に関する研究[j]。中国医学ヘラルド,2021,27(1):127-130+137。
[9] ahmed t, raza s h, maryam a, et al。神経保護剤としてのginsenoside rb1:レビュー[j]。brain research bull - etin, 2016, 125: 30-43。
[10] mohanan p, subramaniyam s, mathiyalagan r, et al。ギンセノシドrb1、rg1、およびrg3の分子シグナルとその作用機序[j]。 journal of ginseng re - search, 2018, 42(2): 123-132。
[11] o ' brien m s, mcdougall j j .変形性関節症の開発のためのリスク要因としての年齢と弱さ[j]。2019年メカニズムofAgeing開発180:21-28。
[12] linn s, murtaugh b, casey e .変形性関節症の発症における性ホルモンの役割[j]。p & r, 2012, 4(5): s169-s173。
[13] francisco v, perez t, pino j, et al。生物力学、ob- esity、および変形性関節症。adipokinesの役割:堤防が壊れるとき[j]。 journal of orthopaedic research 2018, 36(2): 594-604。
[14] alizai h, roemer f w, hayashi d, et al。変形性膝関節症における軟骨損失の危険因子に関するmriベースの半定量的格付け法を用いた評価の更新[j]。ユーロ-あの、放射线岸谷:ちっちゃな泡が25(3):883-893。
[15] francisco v, perez t, pino j, et al。生物力学、ob- esity、および変形性関節症。adipokinesの役割:堤防が壊れるとき[j]。2018年学術誌「ofOrthopaedicリサーチ、36歳という若さ(2):ギター594-604。
[16] zheng l l, zhang z j, sheng p, et al。metabの役割-軟骨細胞機能不全におけるolismと骨関節炎の進行[j]。^ a b c d e f g h i『官報』第2021266号、大正6年6月21日。
[17] zhai g j,変形性関節症における代謝経路の変化[j]。^アポロドーロス、2019年9月1日、11-22頁。
[18] wang h, wang q, yang m, et al。変形性関節症の進行中の組織形成と自然免疫:滑膜炎は軟骨の分解に影響するか[j]。journal of cellular physiology, 2018, 233(2): 1342-1358。
[19] skou st、roos e m、膝および股関節の変形性関節症患者に対する理学療法: 監督と 積極的な治療が現在のベストプラクティスである[j]。clinical and experimental rheumat—ology, 2019, 37(120): 0112-0117。
[20] ヤンx、リンxj。変形性関節症の治療に関する研究の進展[j]。中国整形外科病理学会誌,2019,34(9):900-903。
[21] hermann w、lambova s、muller-ladner u、変形性関節症に対する現在の治療法[j]。現在のrheumat - ology reviews, 2018, 14:08 -116。
[22] zhu n, hou j, ma g, et al。network pharmacology identif- ies the mechanisms of action of shaoyao gancao decoction in treatment of osteoarthritis[j]。medical science monitor, 2019, 14(25): 6051-6073。
[23] culliford d j, maskell j キラン、 らthe life—time risk of total hip and knee arthroplasty: results from the uk general practice research database [j]。^『仙台市史』、仙台市、2012年、20 - 20頁。
[24] hou pw, fup k, hsu h c, et al。伝統的な中国のmedi-膝の変形性関節症を有するcine入院患者[j]。^『人事興信録』人事興信録第5版、人事興信録第5版、2015年、182-196頁。
[25] zhu q g, li j h, fang m, et al。中国式マッサージの効果(tui na)膝変形性関節症患者における等速筋強度に対する影響[j]。2016年漢方医学誌ofTraditional 36(3): 314-320。
[26] wing s s, wai t s, wen c, et al。中国語の局所適用 herbal medicine DAEP を the ラットにおける骨関節炎性膝痛[j]。^『中国医学』、2019年、14:55。
[27] pan b, zhou y, fang f, et al。変形性関節症の国内外における研究状況と治療の進捗[j]。中国基礎医学研究会,2019,27(5):861-865。
[28] cheng w d, wu d y, zuo q, et al。ginsenoside rb1 pre- ventsヒト関節軟骨細胞におけるインターロイキン-1β誘導炎症およびアポトーシス[j]。^ international orthopaed - ics, 2013, 37(10): 2065-2070。
[29] aravinthan a, hossain m a, kim b, et al。ginseno側rb1は、閉経後ラットにおいて、軟骨の分解を防止することにより、モノヨードアセトン酸誘発性変形性関節症を阻害する[j]。^『仙台市史』通史編2(通史編2)282 -294頁。
[30] gao z .薬用植物高麗人参の有効成分であるギンセノシドrb1が変形性関節症の炎症およびプロテオグリカン分解に及ぼす影響[j]。分子植物育種,2022,20(14):4800-4806。
[31] wang w . notchシグナル伝達経路を介したginsenoside rb1によるマトリックスメタロプロテアーゼ13の調節に関する実験的研究[d]。2015年、重慶医科大学教授。
[32] hossain m a, alam m j, kim b, et al。ギンセノシドrb1は、ウサギでのofp-akt、p-p38、p-p65シグナル伝達の下方制御によって骨軟骨の破壊を防ぐ[j]。Phytomedi - cine、2022年、100:154039。
[33]黄チャガントカイ県。ラットの変形性関節症に対するギンセノシドrg1の治療効果と関連機序[d]。2015年、南京医科大学教授。
【34】huangym, wu dy, fan wm。pi3k / aktシグナル伝達を介したil-1b誘導ミトコンドリア-アクチン化アポトーシスによる軟骨細胞上のrg1のギンセノシドの保護[j]。分子細胞生化学,2014,392(1):249-257。
[35] cheng w d, jing j h, wang z, et al。Chondroprotective効果 of ginsenoside Rg 1 in human osteoarthritis chond- rocytes and a rat model of anterior cruciate ligament transec- tion[j]。^ a b c d e f g h i(2017年)3- 3頁。
[36] won h j, kim h i, park t, et al。非臨床薬理学-ギンセノシドの運動挙動[j]。journal of ginseng re - search, 2019, 43(3): 354-360。
[37] so m w, lee e j, lee h s, et al。ヒト骨関節炎軟骨細胞に対するnoside rg3の保護作用[j]。2012年現代内科、23(1):・アイバーソン。
[38] ma c h, chou w c, wu c h, et al。ギンセノシドrg3 - tenuates TNF-a-Induced ダメージ in chondrocytes sirt1を介した抗アポトーシスおよび抗炎症機構の制御を通じて[j]。^ a b c d e f g h i(2017年)10 - 12頁。
[39] xu h l, chen g h, wu y t, et al。ginsenoside roは、pamnr人参のoleアノリックサポニンであり、toll様受容体4シグナル伝達経路を直接阻害することによって抗炎症作用を示す[j]。^『仙台市史』通史編、通史編、2016年、166 -166頁。
[40]張X H X X,徐t Ginsenoside Ro - terleukin-1を抑えるβ-induced アポトーシスを and inflammation in nf-kbを阻害するラットの軟骨細胞 [J]。 中国自然医学会誌,2015,13(4):283-289。
[41] lee s y,ギンセノシドによるマトリックス金属プロテアーゼ阻害の抗転移および抗炎症作用[j]。バイオテクノロジー医薬品、2021年まで、9(2):198-218。
[42] lee j h, lim h, shehzad o, et al。ギンセノシドは関節軟骨細胞のマトリックス金属プロテアーゼ13の発現を阻害し、軟骨の分解を防ぐ[j]。欧州薬理学会誌,2014,724(1):145-151。
[43] yang n, zhang x, li l f, et al。ギンセノシドrcは、生体内でのovariectomy-induced osteoporosisにおける骨形成を促進し、in vitroでは骨原性分化を促進する[j]。international jour - nal of molecular sciences, 2022, 23(11): 6187-6209。
[44] li l, li x, si y, et al。ギンセノシドrb2が関節軟骨細胞を酸化ストレスから保護する機構の研究[j]。中国整形外科学会誌,2018,26(9):845-849。
[45] zhang p . ginsenoside-rg5 変形性関節症のラットモデルでは、軟骨細胞のアポトーシスと軟骨マトリックスの分解を阻害した[j]。腫瘍记事、2017年、37(3):1497-1502。
[46] kim y o, lee s w, kim d h, et al。rheuma- toidや骨変性疾患などの骨疾患を予防または治療するための医薬品compo sitionは、有効成分としてのginsenoside rdとginsenoside reからなる複合ginsenosideから構成されています:kr1856477-b1 [p]。2018-05-14。
[47] siddiqimh, siddiqi mz, ahn s, et al。ギンセノシドrg5の刺激作用:rk1 マウスの骨芽細胞mc3t3-e1細胞について[j]。2014年Phytotherapy研究、28:1447-1455。
[48] su j, zhou r, wang m, et al。変形性関節症におけるキンチリウマチ製剤の有効成分と作用機序をネットワーク薬理学に基づいて予測[j]。中国現代伝統中国医学ジャーナル,2022,24(3):476-487。
[49]衡ケ。rg1による酸化ストレス阻害によるホルモン誘発大腿骨頭壊死の予防に関する実験的研究[d]。『南京医科大学』南京医科大学、2018年。
[50]夏ganqing、周panghu。酸化ストレス応答と変形性関節症の相関と抗酸化ストレス薬の応用に関する研究[j]。難病会雑誌』は2021年まで20(1):94-98。


 英語
英語 フランス
フランス スペイン
スペイン ロシア
ロシア 韓国
韓国 日本
日本




