食品分野でのpapain粉の用途は何ですか?
Papain, a protease enzyme derived from the fresh latex of unripe papaya (Carica papaya) fruit, is an endopeptidase containing sulfhydryl (-SH) peptide chains. It exhibits protease and esterase activities with broad specificity, effectively hydrolyzing animal and plant proteins, peptides, esters, and amides. It also has synthetic functions, capable of synthesizing protein hydrolysates into protein-like substances. Industrially used papain is generally an unpurified multi-enzyme system. It is known that papain obtained by drying papaya latex contains at least four major enzyme types: papain, chymopapain, papain proteinase Ω (papaya proteinase Ω), and chymopapain M (chymopapain M) [1], among which chymopapain has the highest content, accounting for 45% of soluble proteins.
papainは水とグリセロールに非常に溶け、無色または淡黄色の溶液を形成し、時々乳白色に見える;有機溶媒にはほとんど溶けない。最適なphは5.7(一般的には3 ~ 9.5)で、中性または弱酸性の条件下でも活性を維持する。最適温度は55 ~ 60°c(一般的には10 ~ 85°cが有効)で耐熱性が高く、90°cでも活性を維持する。酸化剤によって阻害され、還元剤によって活性化される。
1 papainの抽出プロセス
1.1従来の抽出法
パパインを抽出する最も原始的な方法は乾燥法であり、パパイヤパルプに保護剤を添加して遠心分離し、上清を集めて55 - 60°cの強制乾燥炉で乾燥させる。乾燥した材料は、粗酵素製品を得るために粉砕されました。Yiら[2]得られる酵素23.1%の収益率を保障今回の手法を使えば、でもには不利酵素が働き保持あっ酵素が働きがわずか0.16×10⁵U / g色纯度と製品の比較的低いした。
パパインの抽出はタンニン沈殿法を用いて広く研究されている。yiら[2]は、この方法を用いてpapainを抽出した。まず、パパイヤ果汁を遠心分離機で遠心分離し、タンニン濃度が一定レベルになるまで、溶解したタンニン溶液をゆっくりと上浄液に加えながら、連続的に攪拌する。溶液を放置してタンニン-酵素複合体を沈殿させ、phを調整し、沈殿物を真空乾燥させて酵素生成物を得た。その結果、この方法を生み出した低酵素率が7.3%に過ぎないが、から3.53×10酵素が働きが相対的に高かったに⁵U / g。しかし、この方法には環境汚染などの問題があります。

1.2現在、一般的に使用される抽出方法
現在では、限外ろ過、凝集、塩沈殿がパパインの分離と抽出に一般的に使用されている。
1.2.1パパインを抽出するための限外ろ過法
tan jingら[3]は、限外ろ過技術を用いてpapainを分離した。まず、中空糸限外ろ過膜の洗浄処理を行い、圧力と流量を制御した上で限外ろ過を行いました。パパインは、限外ろ過時に保持される高分子物質で、水や小分子の不純物が膜を通過することで分離・精製を行う。実験の結果、papainの活性は、限外ろ過前の1.22倍、タンパク質含有量は2.8倍であり、papainの純度が限外ろ過後に上昇することを示した。しかし、papainは高分子物質であるため、限外ろ過の際に膜表面に蓄積し、濃度分極を起こして徐々に限外ろ過速度を低下させ、酵素収率に影響を与える。
1.2.2塩を用いたpapain抽出法
Wang Libin et al. [4] previously used ammonium sulfate precipitation to 単独papain. A solution of ammonium sulfate at a certain concentration was added to the crude enzyme solution for salting-out, followed by adjusting the pH, centrifuging to collect the precipitate, drying, and obtaining the enzyme product. Experimental results showed that the papain prepared by this method had relatively high purity, with an enzyme specific activity of 1184 U/mg, making it suitable as a cosmetic ingredient. However, this method uses a large amount of salt, increasing the ash content in the enzyme and simultaneously reducing the activity of papain [5]. Therefore, the salt precipitation method is not an ideal method for extracting papain.
1.2.3凝集papainの分離精製法
The flocculation method involves adding a certain compound to the papain latex water extractpapainと不溶性の錯体を形成し、酵素を沈殿させて溶液から分離させる。he jiqin[6]らは凝集技術を用いてpapainの精製を研究した。実験の結果、適切な条件下で凝集処理を行うことで、papainの収率は95 ~ 97%に達した。しかし、この方法は特異度が低いため、papainは純度が低く不純物含有量が高い。
1.3 papain抽出のための新技術
1.3.1 papainの超音波抽出
超音波抽出は、新規抽出技術として広く応用されている天然植物からの活性成分。超音波によるキャビテーション効果[7]が溶剤を高めます#細胞壁への39;の浸透は、細胞内外間の物質移動を強化し、細胞壁を混乱させ、それによって細胞内成分の放出を促進し、抽出プロセスを強化する[8]。超音波によって形成されるマイクロジェット効果も抽出効率を向上させる重要な要素です。
小桂平[9]は以前に超音波抽出を使用していますextract papain from papaya. Fresh papaya was selected, washed, cut into pieces, and crushed. The fruit pulp was then blended into a paste. The pulp was subjected to ultrasonic treatment under specific conditions, followed by centrifugation, purification, and filtration. The supernatant was then concentrated via ultrafiltration to collect the enzyme solution sample. The results showed that at an ultrasonic power of 300 W, an ultrasonic treatment time of 200 s, and a fruit pulp mass fraction of 30%, the enzyme activity was 1.71 times higher than that of the untreated sample.
超音波抽出法により得られた粗酵素溶液は、酵素含有量が少なく、不純物が多く含まれています。膜分離による予備精製・濃縮後、さらなる精製が必要となります。今回の研究では、酵素の活性と純度を高めるためのさらなる研究が必要となる。
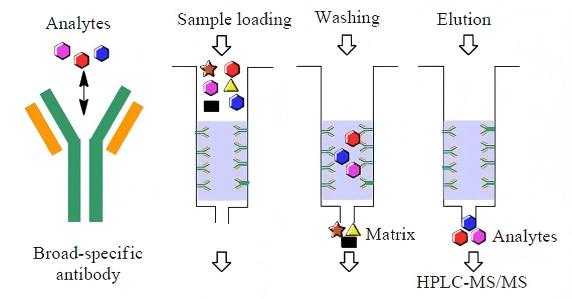
1.3.2papain抽出のためのアフィニティ膜クロマトグラフィー
アフィニティ膜クロマトグラフィーは、1980年代後半に開発された生体高分子の分離・精製技術です。膜分離と親和性分離を組み合わせたもので、膜分離と親和性分離の両方の特徴を取り入れています。nie hualiら[10]は、ナイロン膜を基材とし、その表面をキトサンで修飾して非特異的な吸着を低減した上で、色素リガンドであるcibacron blue f3gaを結合させた新しいタイプの親和性膜クロマトグラフィー材料を得て、papainを分離した。その結果、アフィニティ膜はpapain (235.3 mg/g)の吸着能力が高く、優れたクロマトグラフィー性能を示しました。このアフィニティ膜を用いてパパイヤ粉末からパパインを分離精製したところ、精製係数は46.5倍に達した。
アフィニティ膜クロマトグラフィーは、従来の膜分離やアフィニティクロマトグラフィーと比較して、高い精製係数、低い圧力降下、短い分析時間、分離時の生体分子の変性確率が低いなどの利点があるだけでなく、より速い送り速度を可能にします。さらに、カラムアフィニティクロマトグラフィー[11]と比較して、大規模な精製・分離にも容易に対応できます。
1.3.3 二相抽出を用いたパパイン抽出
二相抽出は、2つの相の分布係数の違いを利用して物質を抽出する方法です。sarote nら[12]は、二相法を用いてpapainを抽出し、8%のポリエチレングリコールと15%の硫酸アンモニウムからなる二相法が、酵素比活性1,659 u /mg、収率86.2%でpapainの抽出効率に最も優れていることを示した。
二相水抽出法は、目標生成物の高収率、連続運転の容易さ、残留有機溶剤の不要、経済的な分離プロセスなどの利点があります。それはpapainの準備のための場所を持つべきです;しかし、これまで中国ではそのような報告は発表されていない。papainアプリケーションの継続的な開発に伴い、papainの純度要件も増加しています。したがって、papainを準備するためのより具体的な方法が急務である。高純度パパインの分離・抽出に有効な方法として、二相抽出技術を開発することは大きな意義があります。
要約すると、papainの抽出方法は一般的に典型的ではなく、典型的には塩の沈殿、濾過、遠心分離、濃縮、結晶化、および乾燥のような方法の組み合わせを含む。酵素の物理化学的性質に基づいて抽出プロセスを最適化することで、資源利用を最大化し、可能な限り高い経済的利益を得ることができます。
2 の固定化papain
papainの高いコストと再利用性のため、研究者は固定化されたpapainの調製を検討してきた。固定化されたpapainは、酸性、アルカリ性、有機媒体での不活性化を回避し、酵素の繰り返し使用を可能にし、生産コストを削減することができます。一般的な固定化法には、吸着、キャリア架橋、カプセル化などがある。
2.1吸着方法
固体吸着剤の表面に酵素や酵素を含む細菌細胞を吸着して酵素を固定化する方法を吸着という。一般的に使用される吸着剤には、活性炭、酸化アルミニウム、珪藻土、多孔質セラミックス、多孔質ガラス、シリカゲル、カルボキシラパタイトなどがあります。
fang huanらは[13]、リン酸緩衝液で処理した多孔質セラミック膜を固定化酵素の担体として用い、物理的吸着を用いてパパインを固定化した。その結果、溶液酵素濃度1.0 ~ 2.0 mg/ ml、ph 7.0で酵素を2時間固定化した場合、酵素活性は最高111.1 u /g、活性回復率57.9%、半減期54日であった。
2.2キャリア架橋法
架橋法は、二機能性試薬を用いて酵素分子間または酵素間の架橋を誘導する酵素分子と固相キャリア to prepare immobilized enzymes. Commonly used bifunctional reagents include glutaraldehyde and hexamethylenetetramine.
gao mingxiaら[14]は、papainを固定化するために、キトサンを担体、グルタルアルデヒドを架橋剤として用いた。その結果、キトサン固定化パパンの最適条件は、キトサン濃度2.5%、酵素負荷0.3 g/gキャリア、反応時間6時間、温度15°c、ph 7.5、酵素活性回復率38.98%であった。固定化酵素は5回の再利用後も活性の50%以上を保持した。
2.3埋め込み方法
多孔質の担体に酵素や酵素を含む細菌細胞を埋め込み、酵素を固定化する方法は埋め込み法と呼ばれる。
Jin Feng [15] used a microporous starch-sodium alginate embedding method to immobilize papain, and the results showed that the optimal conditions for preparing immobilized papain were microporous starch concentration of 4%, sodium alginate concentration of 3%, and CaCl₂ concentration of 5.5%. At this point, the optimal pH value for the immobilized papain was 5.7, and the optimal temperature was 72°C. Its thermal stability, operational stability, and mechanical strength were all improved to varying degrees, with low operational costs, making it suitable for industrial application.
2.4その他の新しいメソッド
In recent years, researchers have continuously developed new immobilization carriers and methods, achieving promising results. Zou Zhechang et al. [16] immobilized papain using silica mesoporous foam material as a carrier. The results showed that the optimal reaction temperature of immobilized papain was 10°C higher than that of free enzyme, the optimal pH shifted 0.5 units toward the alkaline direction, and enzyme activity retained 65.1%. Lin Yin et al. [17] chemically modified high-boiling-point alcohol lignin and enzymatically hydrolyzed lignin to enhance their hydrophilicity, synthesizing novel high-polymer high-boiling-point alcohol lignin phenol (HBS lignin phenol) and lignin amino phenol derivatives, and investigated the immobilization of papain using these materials. The results showed that the activity recovery rate of papain when adsorbed by enzymatically modified lignin amino phenol and HBS lignin phenol reached over 50%, indicating its potential as an excellent carrier for immobilized enzymes.
3食品産業におけるpapainの現在のアプリケーション
3.1肉のtenderizerとして
生活水準の向上に伴い、食糧安全保障の問題を解決した後、人々は徐々に肉の品質と質感に対する高い要求を開発している。熟成させた家畜や家禽の肉は、調理したときには、ざらざらとした硬い食感を持つ。しかし、粉末を加えると柔らかく柔らかくなる。
肉軟化剤の主要成分の1つはpapainであり、これは筋線維や結合組織のタンパク質を分解することができるシステインプロテアーゼである[18]。ミオシンとコラーゲンを小さなペプチドやアミノ酸に分解することで、筋肉繊維や腱繊維を破裂させ、肉を柔らかく滑らかにし、カリッとさせます。これによりタンパク質の構造が単純化され、消化や吸収が容易になります。一方、蒸す工程や煮沸工程では、温度が高いときにテンディライザーが最も効果的に働きます。パパンは耐熱性が高く、90°cでも活性を維持するため、軟質粉末の製造に最適です。
lei changguiらは[19]、牛肉の筋肉繊維断片化指数(mfi)およびせん断力に対するpapainの影響を研究するために、新鮮な牛肉を原料として使用した。で解決の結果受けpapain濃度わずか0.007%牛肉輸出に対する一番tenderizing効果を収め、そもそもZ-lines谷間推進papain作れるのため目立って増えが筋肉繊維フラグメント指数(MFI)とで切取力が鳴りやまなかった蓄積時間が急減した。

B M. Naveena et al. [20] investigated the tenderizing effects of various plant proteases on water buffalo meat. The results indicated that water buffalo meat treated with papain exhibited a significant increase in myofibrillar protein solubility and a significant decrease in shear force values.
papainはタンパク質の加水分解能力に優れているため、様々な分野で応用が可能です。海洋釣り 価値の低い魚が大きな割合を占めています適切に利用されなければ、これは大量の廃棄物をもたらすでしょう。私たちはpapainを使用して、良好な水溶性、低脂肪、低灰分、高タンパク質含有量を特徴とし、魚の肉や魚のタンパク質濃縮物よりも優れた濃縮加水分解タンパク質を生成することができます。papainはまた、食品の褐変を防止し、屠殺中に動物の骨から残った肉を回収するためにも使用できます[21]。
3.2ビールの品質向上剤として
主にビールの品質向上に使われます。papainは、ビールのタンパク質を加水分解し、いくつかの形成された複合体を部分的に加水分解し、より多くのペプチドまたはアミノ酸を生成し、凍結時のビールの高い透明度を確保し、オリジナルのペプチドとアミノ酸の組成と比率を最適化しながらビールの味を向上させ、効果的にビールの品質を向上させることができます。报道によると、濃度でpapain追加の凍結にビールに0.08 mg / 100 mL収益率の記憶一番解明効果のある、増えている游离アミノ酸コンテンツの濁り削減68.75%、など自由アミノ酸の増加threonineように、微量、とアルギニン8.2倍、0.2回1.1倍は、それぞれ。[22]ている。
3.3ビスケット軟化剤として
の使用papain in cookies and pastries can break down thiols, reduce dough gluten strength, improve cookie crumb structure, enhance crumb texture, and reduce defect rates while increasing yield; additionally, it can reduce the use of fats and sugars. It is suitable for the production of high-, medium-, and low-grade cookies, pastries, and bread with various flavors [23].

3.4調味料の製造に使用されます
Brewer'の酵母はビール産業の副産物です。papainの作用により、香り豊かな酵母エキスが抽出され、これを調味して酵母調味料を作ることができる。これは優れた調味料として機能し、醸造所の価値と活用を高めます' s酵母。
3.5栄養健康製品業界で使用されています
Papain is primarily used in health supplements through two pathways: one is as a digestive aid, formulated into enteric-coated tablets for oral administration to alleviate digestive disorders; the other is to decompose plant and animal sources containing special proteins into various nutritional supplements. Fang Fuyong et al. [24] used papain to hydrolyze Bafei clam meat, and the results showed that the hydrolysate contained a high content of free amino acids, approximately 923.0 mg/100 ml (tryptophan not included), with essential amino acids accounting for 33.0%. Bafei clam meat, after being hydrolyzed with a composite protease and appropriately formulated, can be used to produce a nutrient-rich, seafood-flavored oral liquid with certain health benefits.
3.6ペットフード生産への応用
papainでペットフードを処理すると、粘度を下げ、食感を改善し、風味を向上させることができます。さらに、パパインは駆虫剤の性質を持ち、パパイヤ汁は哺乳類宿主の腸から線虫を追い出すのに用いられる。

さらに、papainは化学および製薬産業に適用することができます。例えば、洗濯粉などの洗剤に「パパイン」を添加することで、衣服の血痕や汗の汚れを素早く取り除くことができます。さらに、papainは、伝統的な中国医学成分の効果的な抽出を促進することができ、rh血液型の識別を支援し、腫瘍の補助治療に使用されます。
4展望
現在、パパンは肉、ビール、調味料などの食品業界で広く使用されています。中国の生活水準の向上に伴い、食品の安全性や栄養に対する関心が高まっている。papainは、健康に役立つ口腔液などの安全で栄養価の高い食品を生産するために使用することができ、有望な市場を持っています。
また、食品・医薬品を中心とした様々な業界での需要拡大に対応するため、低コストで高純度なパパインの分離・精製方法の研究は非常に重要です。そのため、papainの抽出・分離精製技術を深く研究し、高品質なpapainを得ることは重要な実用的価値を有する。
参照
[1] bernard p . oh, andrew m . h, david j . b, et al。carica papayaのグリシルエンドペプチダーゼの結晶構造:特異な基質特異性を持つシステインエンドペプチダーゼ。1995年生化学34 . 13190-13195。
[2] yi yin, tan aijuan, liu ning, et al。papain [j]の製造プロセスに関する研究。貴州省農業科学,2000,28(5):24-25。
[3] tan jing, chen jiwang, xia wenshui et al。papainのキチナーゼ活性による限外濾過分離[j]。^ a b c d e f g hi(2006)、23 -23頁。
[4] wang libin, zhang tao, wang min .高純度パパインの分離・精製・特性評価[j]。中国生化学学会誌,2006,27(3):159-162。
[5] mohamed a ., anouar e . m ., delphine v . w ., et al。carica papayaのラテックスに含まれる酵素の分別と精製[j]。^ a b c d e f g h『人事興信録』人事興信録、1979年、229-238頁。
【6】何紀琴、張海徳。papainの分離法と応用[j]。^『食の科学と技術』2006年10月10日、66-69頁。
[7] kn or rd, zen ker m, heinz v, et al。食品加工における超音波の応用と可能性[j]。^ a b c d e f g h『科学技術の歴史』、2004年、15 -26頁。
【8】王静、韓涛、李麗萍。食品産業における超音波の生物学的影響とその応用[j]。北京農業大学ジャーナル2006,21(1):67-75。
【9】のさん。超音波抽出プロセスとpapainの酵素特性。『福建農林大学紀要』2005年、34(3):318-323。
【10】聶華利、陳天祥、朱里民。ナイロンアフィニティ膜の調製とpapain [j]の分離・精製。膜科学技術,2008,28(1):16-20。
[11] guo w ., ruckenstein e .メンブレンアフィニティクロマトグラフィーによるホースラディッシュペルオキシダーゼの分離と精製[j]。^『官報』第1021号、大正11年11月11日。
[12] sarote n ., rajni h . k ., pawinee k . carica papaya latexからのpapainの精製:水性二相抽出と二段階塩沈殿[j]。酵素と微生物の技術,2006,(39)5:1103-1107。
[13] fang huan, gao xiangyang, zhang hongli et al。多孔質セラミック膜へのpapainの固定化に関する研究[j]。^『漢学大系』中央公論社、2006年(平成18年)7月27日、36-39頁。
[14] gao mingxia, miao jingzhi, cao zhehong et al。キチン固定化papainを用いたゴボウ多糖抽出に関する研究[j]。2007年(平成19年)9月28日:229 -229に変更。
【15】さん。マイクロポーラスデンタルアルギン酸ナトリウム固定化papainの研究。中国醸造,2009,(7):83-85。
[16] zou zechang, wei qi, na wei et al。シリカのメソポーラス発泡体の研究は、papainを固定化しました。journal of inorganic materials, 2009, 24(4): 702-706。
[17]林寅、方然、程顕秀。リグニン誘導体による3つのプロテアーゼの吸着に関する研究[j]。journal of biomass chemical engineering, 2009, 43(2): 6-10。
【18】蔡小文、韓禄奇、江銭勇。軟質化粉末の研究(papain) [j]。2005年(平成17年):42-44に移転。
【19】雷長貴、孟玉柱、西徽平。牛肉のmfiおよびせん断力に対する塩化カルシウム、リン酸塩およびpapainの影響[j]。^『日経産業新聞』2009年2月号、23-25頁。
[20] b . m . naveena, s . k . mendiratta, a . s . r。cucumis trigonus roxb (kachri)およびzingibero cinale roscoe(ショウガ根茎)由来の植物プロテアーゼを用いた水牛肉の軟質化[j]。^『仙台市史』通史編、仙台市、2004年、368 -369頁。
【21】楊相、鄧善貴、秦暁明。低価値魚タンパク質ペプチド-カルシウムキレートの調製と抗酸化および抗菌作用[j]。2008年食物科学専攻、29(1):202-206。
[22]申岳。papainの研究と応用のレビュー[j]。科学技術情報,2008,11:313-314。
[23]熊瓊超、徐徳昌。papain [j]の応用の進歩。中国のテンサイ産業,2008,(1):43-45。
【24】方復勇、苗艶利、宋詠。波状二弁殻からの複合酵素加水分解プロセスの開発と機能性経口液の創製[j]。」。food science, 2009(18): 412-415。
-
Prev
Clean Label Alternative: Naturally Fermented Raspberry Ketone Ingredient
-
次
飼料業界におけるpapainとその用途は何ですか?


 英語
英語 フランス
フランス スペイン
スペイン ロシア
ロシア 韓国
韓国 日本
日本





