黒ニンニク発酵過程における風味変化の研究
ニンニクには、アリシンやs-アリル- l-システイン(sac)などの有機硫黄化合物が豊富に含まれており、抗菌、抗酸化、抗がん、抗糖尿病、抗炎症作用のある有効成分である[1]。しかし、ニンニクの細胞構造が破壊されると、これらの化合物はアリルメチルスルフィドやアリルメルカプタンなどの揮発性物質に変換され、ニンニクに強い辛味と刺激臭を与える[2]。
Fermentatiにcan effectively 減らすのpungent odor のニンニクとalso make のtexture のニンニクsofter とchewy, similar にjelly [3]. Black ニンニクis をによってfermenting 新鮮なニンニクで高いtemperatures とhigh humidity. Studies [4] have found その黒ニンニクcan effectively alleviate のsymptoms のdiabetes patients, と◆anti-cancer ability とpotential にreduce のrisk のcardiovascular disease are even stronger than garlic. This article intends to focus にの変化でchemical compositiにと味化合物中のprocessing 黒garlic, focusing にの鍵factors that affect ◆flavor formation, deeply analyze the flavor characteristics の黒garlic, とprovide a basis ためimproving the 品質のブラックニンニクの商品.
1黒ニンニクの処理中の主な化学成分の変化
Black garlic is a deep-processed ニンニクproduct made によってfermenting 新鮮なニンニクat a certaで温度(50–90°C) とhumidity (70%–90%) for a certaでperiod のtime [5–7]. This fermentatiに過程involves a variety のchemical reactions, including the メイラードreaction, 熱degradatiにreaction, oxidatiにreaction, polymerizatiにreaction, rearrangement reaction, とenzymatic catalysis reaction. These reactions ca使用変化でthe chemical composition, which でturn affect the flavor, color, とnutritional 文化財のthe garlic. In terms のcolor, 発酵changes ニンニクfrom white to black, hence the name 黒garlic.
図1に示すように、発酵後にニンニクの化学組成が変化します。還元糖の含有量,有機酸,アルカロイド,ポリフェノール,メラノイジンおよび5-ヒドロキシメチルフルフラール(5- hmf)増加します,水分の含有量ながら、,脂質,アリシンおよび多糖類は減少します[8]。これらの中で、ポリフェノール、5- hmf、アルカロイドの増加は黒ニンニクに強い抗酸化、抗ウイルス、抗がん作用を与えることができます;アリシンとガリシンの減少は、黒ニンニクの刺激臭を減らすことができます;また、発酵由来のメラノイジン、チオフェン、フラン、ピラジンは、黒ニンニクに独特の香ばしさ、甘味、キャラメル風味を与えることができる[9]。
1.1有機硫黄化合物の変化
ニンニクには独特の辛味のある香りがあり、これは主にアリシンや揮発性硫黄化合物などの物質の存在に起因する[10]。有機硫黄化合物を図2に示すように、ニンニクで行動deamidationコンバート結びつける必要があります。γ-glutamyl peptidaseにγ-L-glutamyl-S-allyl-L-cysteine、によって変換deamidationする不親切やサクラメントS-oxidationγ-L-glutamyl-S-allyl-L-cysteine-S-oxide、そしてS-oxidationまたはdeamidatiにS-allyl-L-cysteine塩化(シン」。アリシン)[11]。アリルチオ硫酸は、ニンニクを粉砕またはすりおろした後、アリナーゼによって加水分解されてデヒドロアラニンとアリルスルホン酸が生成する無色無臭の物質である。2つのアリルスルホン酸は自発的に凝集してアリシンを形成し、これがニンニクの主な供給源となる#39;の刺激臭[12]。アリインは不安定で、硫化アリルジアリルジスルフィド、二硫化アリルジアリルジスルフィド、三硫化アリルジアリルジスルフィドなどの揮発性スルフィドに分解することがあります[13]。
発酵は様々な化学反応を伴うため、食品の風味を変えることができる[14 - 16]。発酵中には、熱処理によってアリナーゼが不活性化され、アリシンの生成が減少するため、黒ニンニクには刺激臭がありません[17]。さらに、アリシンは、黒ニンニクではニンニクよりも6倍高い、安定で無臭のs-アリル- l-システイン(samc)に反応することによって変換することができます[18]。二硫化アリル、三硫化アリル、三硫化ジプロピルは、ニンニクと黒ニンニクの両方の硫黄化合物に見られる。ニンニクからはアリシンのみが検出されるが、黒ニンニクからは2-アセチル-1-ピロリンが検出される[18];硫化アリルメチルトリスルフィド、硫化アリルジスルフィド、二硫化アリルジスルフィド、三硫化アリルジスルフィドなどの硫黄化合物、およびその他の硫黄含有化合物の含有量は、黒ニンニクで徐々に減少する[20]。
1.2炭水化物の変化
The carbohydrate コンテンツのニンニクis about 33%, とit is mainly composed のwater-soluble sugars とfructans. The fructans でニンニクare keto-sugars composed のfructose とglucose でa ratio のabout 14:1 [21]. Garlic polysaccharides are degraded 中fermentatiにto form various monosaccharides (e.g. glucose, fructose, etc.) or disaccharides [22]. Li et al. [23] showed that 中the processing の黒garlic, the total amount のpolysaccharides decreases によってabout 30%, とis converted into monosaccharide components, mainly fructose, galactose とgalacturonic acid, with a molar ratio の307:25:32. In addition, high temperatures とlow pHcan promote the hydrolysis のsucrose と生産glucose とfructose, which give 黒ニンニク◆sweetness [24]. Black ニンニクalso has a sour taste, which is due to the increase でorganic 酸content 中polysaccharide 劣化[25].
炭水化物はメイラード反応の前駆体である。amadori (n-置換1-アミノ-1-デオキシ-ケトース)およびheyns (n-置換2-アミノ-2-デオキシ-アルドース)はメイラード反応の重要な中間生成物であり、メイラード反応の程度を評価するためにしばしば用いられる。また、メラノイジンの形成の前駆体でもある。
アマドリおよびヘインは酸加水分解によって2-フラニルメチルリシンおよび2-フラニルメチルアミノ酸に変換することもでき、これらは黒ニンニクの品質を評価するための重要な指標でもある[26]。メラノイジンはメイラード反応の最終生成物であり、窒素を重合した褐色の炭水化物である。彼らはまた、茶色の顔料として知られており、処理中に黒ニンニクの褐変に大きく貢献していますメラノイジンに加えて、発酵中のメイラード反応も5- hmfを生成することができ、これは食品の炭水化物含有量を評価するために使用することができるさらに、カラメル化によって5- hmfを形成することもできる。zhangらは、5- hmfが黒ニンニクの色に影響を与える可能性があると指摘している[29]。5- hmf含有量が4 g/kgのとき、ニンニクは黒くなり始めます。5- hmf含有量が高いほど黒ニンニクの褐変が深くなり、5- hmf含有量が高すぎると黒ニンニクに苦味が生じる。
1.3その他の化学成分の変化
黒ニンニクの加工中のメイラード反応はタンパク質変性や様々なアミノ酸の形成を引き起こす。酸性条件下では、メイラード反応は酵素反応または非酵素反応によってタンパク質またはペプチドの分解を引き起こし、黒ニンニク中のいくつかのアミノ酸(l-アラニン、l-バリン、l-イソロイシン、l-チロシン、l-フェニルアラニンなど)の含有量を増加させる[24]。liら[23]は、ニンニクを凍結前処理して調製した黒ニンニクのアミノ酸含有量が50.97%減少したことを発見し、黒ニンニクのアミノ酸含有量は処理方法によって異なることを示した。
Lipids can change 中the processing の黒ニンニクdue to oxidation. After ニンニクis 発酵into 黒garlic, crude lipids can be converted into 化合物such as alcohols, aldehydes, ketones とlactones under high 温度とhigh humidity conditions, thereby giving 黒ニンニクa rich flavor, but the crude lipid content is significantly reduced [30].
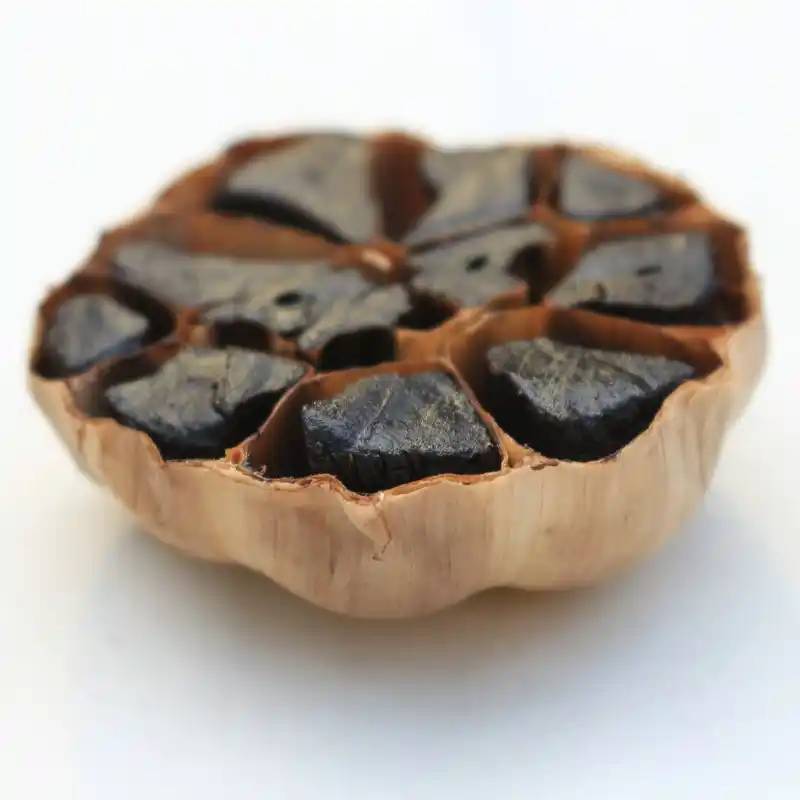

2黒ニンニク加工中の特徴的な風味化合物の変化
食品では、食品に独特の香りを与えることから、風味化合物が特徴的な風味化合物として定義される[31-38]。
表1は、ニンニクの緑と硫黄の風味が黒ニンニクよりも顕著であることを示しています。硫化ジアリル、3-ビニル-1,2-チアゾール、ジメチルジスルフィド、ジメチルトリスルフィドなどの化合物は、すべてニンニクの硫黄の風味やニンニク特有の風味に寄与する。黒ニンニクでは、ローストした甘い香りなどの物質の含有量が増加し、黒ニンニク独特の甘酸っぱい風味に寄与します。黒ニンニクは、アルデヒド、アルコール、揮発性硫黄化合物、ケトン、有機酸などのさまざまな香り成分を含み、ニンニクは主に揮発性硫黄化合物と少量のアルデヒドとケトンを含んでいます[10]。
The 揮発性知りませで黒garlic, such as 2-vinyl-4H-1,3-dithiophene, allyl methyl trisulfide, diallyl trisulfide, 3-vinyl-1,2-thiazole-4-cyclohexene, とdiallyl sulfide, together impart the garlic-like aroma characteristics の黒garlic. 3-Vinyl-1,2-thiazol-5-one, diallyl disulfide とdiallyl sulfide are 特徴flavour 化合物のgarlic. Allyl methyl trisulfide とallyl methyl disulfide are flavour 化合物common to ニンニクと黒garlic. Volatile sulfur 化合物such as allyl trisulfide とdiallyl sulfide have a particularly strong aroma due to をlow threshold values [34].
硫黄化合物に加えて、複素環式化合物も黒ニンニクの重要な芳香族活性物質である。その結果、2(5 h)-フラノン(焦げた)、フランカルボン(キャラメル味)、2-アセチル-1-ピロリン(ローストアーモンド味)、2-フラニルエタノン(バルサミコ酢味)、5-ヘプチリデン-2(3 h)-フラノン(アーモンド味)が検出された。これらの化合物は黒ニンニクに独特であり、その香ばしい香りと甘味の主な原因である。また、黒ニンニクには、1-ヒドロキシ-2-ブタノン(塩味)と3-メチルチオプロパナル(ジャガイモの調理味)という2つのユニークなカルボニル化合物が含まれている。アリルアルコール(調理ニンニク風味)や(e, z)-2,6-ノナディエン-1-オール(キュウリ風味)のような化合物の形成も黒ニンニクの独特の風味に寄与しており、ニンニクとは異なる。3-メチルブタン酸(汗臭)、酢酸(酸味)、プロピオン酸(辛味)などの化合物が黒ニンニクの酸味を増す。発酵は、酸味とうま味を高め、塩味を減少させ[37]、ニンニクの苦味を大幅に減少させる。この変化は、有機硫黄化合物の含有量の減少に関連している可能性があります。
黒ニンニクの風味特性に影響を与える3つの要因
Factors such as ニンニクvariety, planting location, とgrowing conditions have a significant 影響on ◆quality, which でturn changes the 感覚attributes 黒ニンニク[38]. In addition, the nutritional composition のgarlic, the processing 技術の黒garlic (e.g., 前処理methods, fermentation temperature, fermentation time, とrelative humidity), the chemical reactions that occur 中processing (e.g., the Maillard reaction), と内細菌also affect the flavor 品質の黒garlic [39].
3.1栄養要因
3.1.1炭水化物フルクタンは黒ニンニクの品質に影響を与える重要な要因の一つです。黒ニンニクの処理中に、そのフルクタン含有量は84.6%から99.2%と有意に減少した[40]。黒ニンニクのフルクトース含有量はグルコースよりも高く、フルクトースはケトースであり、アルドースであるグルコースよりも低い速度でメイラード反応に関与する[4]。したがって、発酵後、ニンニクの果糖含有量がある程度増加し、黒ニンニク特有の甘い香りの形成に寄与する[42]。また、黒ニンニクの酸味の形成は、熱処理中の炭水化物の発酵と分解と密接に関係している[42]。発酵と炭水化物の分解によって有機酸が生成され、phが低下することがあります[42]。
3.1.2タンパク質とアミノ酸
ニンニクにはタンパク質と必須アミノ酸が豊富に含まれています。高温処理によって黒ニンニク中のタンパク質が変性し、様々な遊離アミノ酸が生成する。黒ニンニクの加工過程では、メイラード反応に関与して芳香物質を合成するため、チロシン、アルギニン、グルタミン酸などのアミノ酸が還元される[43]。さらに、黒ニンニクの処理中にロイシンやイソロイシンなどの分岐鎖アミノ酸の含有量が有意に増加する。これらの遊離アミノ酸は、糖とメイラード反応を起こし、さまざまな揮発性物質を生成することができる[39]。
3.2品質特性
ニンニクの品種、栽培場所、気候条件、土壌特性、降雨量、栽培管理などの要因はすべて、ニンニクとその黒ニンニク製品の品質、香り、官能特性に影響を与えます[44]。異なる起源のニンニクの品質および生理活性化合物は、組成および含有量において有意に異なる可能性がある[45]。通常のニンニクから発酵させた黒ニンニクに比べ、有機ニンニクから発酵させた黒ニンニクは有機硫黄化合物を多く含み[45]、ニンニクの成長時間が長くなると黒ニンニクの5- hmfの含有量が増加する[6]。
3.3プロセス要因
3.3.1前処理方法
一般的な前処理方法には、凍結前処理、高圧前処理、超音波前処理があり、それぞれの前処理方法の影響機構が異なります[46]。凍結前処理は、ニンニクの細胞構造を破壊し、より特徴的な風味化合物の生産を促進し、それによって黒ニンニクの甘味と品質を高めることができる。高圧の前処理は、特定の風味物質を維持または強化するのに役立ち、黒ニンニクの味をより豊かでバランスの取れたものにします。超音波前処理は、抽出し、成分を変換し、香りと風味の物質の形成を促進するのに役立ちます音エネルギー、ニンニクの細胞壁の透過性を向上させます。
その結果,凍結保存(-20°c, 30時間),超音波前処理(28 khz, 2時間),高静水圧前処理(300 mpa, 15分間)により,ニンニクの嚢含有量がそれぞれ6倍,4倍,10倍に増加した[47]。冷凍保管に比べ超高圧前処理、超音波前処理できるのニンニク料理の细胞壁クロスオーバーを大幅に増強より血清の流出共感的γ-glutamyl細胞からtranspeptidaseの断片と反応γ-L-glutamyl-S-allyl-L-cysteine、サクラメント含有率が高いという結果を生んだ黒ニンニク製品[46]。さらに、凍結前処理はニンニクの細胞構造を著しく損傷させ、メイラード反応を加速させ、より多くの5- hmfを生成する。オーミック加熱の非熱効果(110 - 130 v、60 - 80°c)は、フルクタンを加水分解してフルクトースにするのを助け、メイラード反応を加速させ、5- hmfの蓄積を増加させる[48]。
3.3.2発酵温度
Fermentation temperature has a significant effect on the taste とaroma の黒garlic products [29]. As the fermentation temperature increases, the content のaroma precursors such as allicin, SAC とγ-L-glutamyl-S-allyl-L-てgradually decreases [49]. When the fermentation temperature is <60°C, the garlic has not yet completely blackened とits pungent aroma has not yet completely dissipated. When the fermentation temperature is 70°C, 質とflavour のthe 黒garlic are better [49]. When the fermentation temperature is >90°C, the chemical reactions でgarlic accelerate, the reducing 砂糖content decreases, とa bitter とburnt flavour may develop, or even harmful substances may form [39]. Under conditions のa fermentation temperature の75°C とa relative humidity の85%, the content のaroma precursor substances such as γ-aminobutyric acid, SAC とγ-L-glutamyl-S-allyl-L-cysteine changed most significantly, which helped to 強化the flavor quality の黒garlic [50].

発酵時間3.3.3
適切な発酵時間は、化学反応の効率を高めるだけでなく、黒ニンニクの香り成分の豊かさを高め、バランスのとれた味を維持します。70 ~ 80°cで10日間発酵させた結果、ニンニク中のアリシン含有量は11.3 g/kgから2.3 g/kgに減少し、検出不能レベルまで低下した[51]。アリシンの減少は主にsamcへの変換によるものであり,アリインの減少は硫化アリルジアリルジスルフィド,三硫化アリルジアリルジスルフィド等への変換によるものであった。発酵の45日後である4000°Cから黒いニンニク増えたサクラメントコンテンツ196.0μg / g 124.7μg / g [52]また、黒ニンニクのグルコースとフルクトース含有量は、発酵45日目にピークに達した[9]。
3.3.4相対湿度
黒ニンニクの外観と褐変度は、相対湿度と密接に関連しています。湿度が高いと褐変が遅くなり、黒ニンニクはより甘く湿っており、有機酸の含有量が減少します。一方、湿度が低いと化学反応が阻害され、風味化合物の生成が妨げられ、硬い食感になる[53]。黒ニンニクの処理に最適な湿度は80%です[49]。さらに、水の活性はメイラード反応にも影響を与え、黒ニンニクの芳香化合物の形成にも影響を与える[53]。
3.4メイラード反応
メイラード反応は、メラノイジン、チオフェン、ピラジン、フラン、フラノン[54]、5- hmfおよびその他のフルフラール化合物[55]などの様々な複素環性物質を生成する。メイラード反応によって生成される風味化合物は、主に黒ニンニクのローストした香りの原因である。例えば、メイラード反応によって生成される2(5 h)-フラノンは黒ニンニクにトーストのような香りを与え、3-メチルチオプロパナールは調理されたジャガイモに似た風味を与える[10]。メイラード反応は脂質酸化と密接に関連しており、両者の相乗反応は反応中間体の相互作用を促進し、黒ニンニクの風味を豊かにする。
Najman et al. [37] identified various flavor 化合物で黒garlic, such as carbon disulfide, 2-methylthioethanol, 2-methyl-2-propyl mercaptan, 2-octanone, 2-furancarboxaldehyde, α-pinene, 2,3-dimethylpyrazine, 5-methylfurfural と4-hydroxy-5-methyl-3-furanone, which together give 黒garlic a complex aroma のtoasting, caramel, burning とfruit. In addition, 5-methylfurfural and 2-acetylfuran can give black garlic a unique sweet aroma [3]. The intermediate product のthe Maillard reaction, 2-acetylpyrroline, is the maでsubstance that gives black garlic its pleasant aroma [56]. Furfuryl 化合物produced by the Maillard 反応have a sweet characteristic and are key markers that distinguish black garlic from garlic [20]. Organic sulfur 化合物でgarlic are mainly converted into volatile nitrogen-containing compounds such as alkyl sulfides, pyridines, and pyrazines during fermentation, and these compounds do not exist でgarlic [12].

3.5内細菌
内生菌は生物の制御機能だけでなく、植物の成長を促進する。黒ニンニクを形成するニンニクの自然発酵は、その内生細菌の活性に関係している[57]。内生細菌は、ニンニクの発酵を促進し、その味を改善し、より多くの機能性化合物を形成し、それによって保存期間を延長することができる[58]。Suhartiら内[59]孤立エルウィニア属菌などの善玉菌、彼らの右側の、Xanthomonas、Agrobacterium、Rhodostominia、Xylella、Pantoea、Acidiphilus、Burkholderia、Corynebacterium、Streptomyces、促进ブドウ糖の劣化を生成する有機酸化合物などの成分が酒石酸酸コハク酸、リンゴ酸酸や酢酸を刺激し、黒いニンニクに酸味。また、内生菌でもあるバシラス属は、イヌリン型フルクタンのフルクトースへの変換を促進することができます[27];同時に、有機硫化物や5- hmfの濃度が増加すると、バシラス属の種数は減少します。
4結論
ニンニクの発酵過程には、さまざまな化学反応が含まれており、刺激臭を和らげ、黒ニンニク特有の甘酸っぱい香りを形成するのに役立つ。同時に、発酵は黒ニンニクのより機能的な活性物質の形成を促進することができ、それは抗酸化、抗ウイルスおよび抗がん効果を備えています。したがって、ニンニクの深い加工製品として、黒ニンニクは良い市場の見通しと開発の潜在力を持っています。風味剤の開発により、黒ニンニクの風味物質の研究が進んでいるが、依然として問題が多い。その後、黒ニンニク風味物質の標準化された指標と試験方法を確立することができる。黒ニンニクの特徴的な風味物質の生産経路と相互関係をさらに深く調べることができる。ブラックガーリックの風味と栄養の質は、消費者の好みに応じて正確に制御することができます。
参考:
[1]い T, AGGARWAL Aデイ P et al.Medicinal ニンニク、ニンニク精油、ニンニクベースのスナックの治療特性 食品: 更新 審査か[J]。フロンティア で 栄养、2023、10:1120377。
[2] tedeschi p、nigro m、travagli a、他。アルツハイマー病におけるアリシンおよび老化ニンニク抽出物の治療可能性' s病気か[J]。国際学術誌「ofMolecular 科学や2022年、23(13):1374年- 1389年。
[3] MOLINA-CALLEM、PRIEGO-CAPOTE F、徳 CASTROMD l . headspace-gc-ms volatile profile(英語 のblack ニンニクvs 新鮮な ニンニク:発酵に伴う進化と加熱下での挙動[j]。LWT -食品 科学 and 技術を取り入れた80:98-105、2017年です。
[4] SARYON 0, nani d, proverawati a,et al 効果 の black ソロ ニンニク(Allium chinense sativuml) streptozotocin-induced diabetesin Wistar 鼠か[J]。Heliyon、2021年まで、7 (12):e08493。
[5] MANOONPHOL KSUTTISANSANEE U, PROMKUM C et アル効果 の 熱 処理 on S-allyl cysteine content で 黒ニンニクか[J] .Foods 2023 1227年)12(6):。
[6] liu z, kang d c, lixr,et al.Analysis ofvolatile有機化合物 で black garlic made の garlic 電球 後 収穫白く窶れ garlic 葉 at 異なる 成長 時代 基づいて on PCAと headspace-gas chromatography-ion 移動 離イオン化法(HS - GC-IMS) [J]。誌 の 食品 処理 and 22年保存46 (5):e16550。
【7】ターヒル朝 アルアフリがZ FNOSHEEN F et al.Comparative 研究 生と発酵(黒)ニンニクの栄養特性と抗酸化活性の[j]。国際 誌 の 食品 器物や2022年25(1):116-127。
【8】qiu zc, zheng z j, zhang 、栄養面から見るとB、et al.Formation 強化 特徴コンポーネントの で 黒ニンニク:長所を最大化するためのレビュー 人間か[J]。総合评论食物科学専攻や食品安全19(2):801-834、2020。
[9] AOUDEH オズE E KELEBEK H et al.Black garlic アニメ制作: 影響 の 高齢化 temperature and 期間 on 一部のphysicochemical and 抗酸化 及び sugar 内容か[J]。国際 誌 ofFood 科学 and 技術、2023 58(7):3.580-3590。
【10】扬 P、宋 HL、王 L J et al.Characterization の 黒ガーリックの主要な芳香族化合物である 分析か[J]。誌 の 農業 and 食品 化学、2019年67(28):7926-7934。
[11] wakamatsu j, stark td, hofmann t . taste-active maillard 反応 製品 in 焼いた ニンニク(Allium chinense sativum)か[J]。 誌 の 農業 and 食品 化学、2016年64(29):5845-5854。
[12]安倍首相 堀K Y, MYODA T.Characterization of key 香り化合物 in 歳 garlic 抽出 [J]。食品 化学、2020年 312:126081。
[13]安倍首相 堀K Y, MYODA T.Volatile compounds of 新鮮な 処理 ニンニク[J]。実験 and 治療 医学、2020年 19日(2):1585-1593。
[14] HOUXY、王 ジョナサン、DENGNなど al.Research 進歩 on 効果 of 乳酸 acid bacteria on the flavor of the 発酵 野菜か[J]。食品 &機械、2023 39(4):232-240。
[15] GUANQQ、ウン T XIEMY研究 進歩 in 乳酸 酸菌 fermentation technology ofplant-based か[J]。紀要 食品 科学 and バイオテクノロジー41(7):2022年、11。
[16]劉 M、邓 N、李 H et al.Characterization and 比較 味である in 新鮮な and 歳 fermented トウガラシ:影響 of 異なる 品目をか[J]。食品 研究 がいたことは2024年、182:114187てる
[17]トゥランe,シムセクa .への新鮮なニンニクの代替として黒ニンニク reduce off-flavor and enhance 消費者 受付 and セメントペースト中の生物活性特性[j]。journal of food processing and 22年保存46 (2):e16246。
[18]陳 ZX、XUM J、王 C et al.Thermolysis 彼を敬愛し そして、アリインの熱分解化合物[j]。2017年食品化学、223:25-30。
[19] CZOMPAA SZOKE k, prokisch j,et al.熟成(黒)と生ニンニク 虚血/ reperfusion-induced心臓 か[J]合併症。国際 誌 of 分子 科学 1017 19、2018年(4):。
[20] MARTINEZ-CASAS L, LAGE-YUSTY M ヘルナンデスロペス- J.Changes in the 、芳香プロファイル、糖類、 生物活性化合物紫色のニンニクが黒に変わるとき ニンニク[J]。紀要 ^農業・食品化学、2017年、65頁
(49): 10804-10811。
[21]元ぐらい H、孫 L,陳 M, et al.An 分析 of the changes 黒ニンニクの熱処理中の中間生成物について[j]。2018年食品化学、239:56-61。
[22] LINYLUXM)、基善(ぺ HBメトロ・カードとデビッド al.Effect of 凍結 pre治療 黒ニンニクの処理時間と品質について[j]。日本食品工業学会誌,2015,38(4):329-335。
[23]李 M, YANYX、YUQTなど al.Comparison of 生のニンニクと黒ニンニク多糖類の免疫調節作用264.7マクロファージ[j]。誌 of 食品 2017年科学、82(3):765-771。
[24]大人梁 ミシェル・ウィーはタスクフォース(TF) FFルゥ Y et al.Comprehensive ポリオキサミド树脂 分析 熱加工中の黒ニンニクの組成変化について[j]。農業・食品化学誌,2015,63(2):683-691。
[25]やがてアフメド T WANGCK黒 garlic and its bioactive ませんでした 人間 健康 病気: 審査ではか[J] .Molecules 2021、26(16):5028。
[26] ANDRUSZKIEWICZ -一体どう、D'时会擦RN、コレノMなど al. new amadoriおよびheyns短ペプチド由来の化合物が発見されました in 干し ココア 豆か[J]。食品 研究 2020インターナショナル 133:109164。
[27]鄭秋Z Z、張 B et al.Characterization of 成長 文化財 of garlic endophytes and their 役割 in 形成 黒 ニンニク[J]。LWT-Food 科学 and 技術、2021年147:111537。
[28]「胡H、王 Y申 M, et al.Effects of 焼成 要因や調理法 on the quality バター クッキー and the 形成 先進glycation 最終製品(ages)と5-ヒドロキシメチルフルフラール(hmf)[j]。現在の研究結果 食物科学専攻、2022年、5:940-948。
[29] ZHANGXY LINY、LUXMなど al.Effects of temperature on the quality of black garlic [J]。誌 of 農業 and 2016年食品化学96(7):2366-2372。
[30] ZAMORA R,イダルゴ F J.Coordinate 貢献 of 酸化脂質 and Maillard reaction to the nonenzymatic 食品よか[J]食物栄養科学の重要なレビューにおいて05シーズンまで、45(1):49-59た。
[31]孟 X R,高 z W、王 H P et al.Construction サイクリックの揮発性フレーバー強度の評価モデル ビーフシチュー 基づいて on 校長 成分 分析か[J]。食品 &机械、2022年、38(10):29-36。
[32]趙 X,裕 PH、黄 H et al.Investigated by hs-gc - imms紅茶原料の揮発性香料に対する乾燥法の影響[j]。journal of food science and biotechnology,2022, 41(9):104-111。
[33]張 R R, YUXW、欧陽 H et al.Combination of HS - SPME-GC-O-MS and E-nose 明らかに the characteristic スイカの香りの違い 様々な熱処理下の種子[j]。&食糧、機械、2023 39(1):917年(延喜17年)。
[34] cui yw, liu l x, zhang l y,et al of garlic 基づいて on HS-GC-IMS 結合 多変量統計と 分析か[J]。分析方法、2024年16(3):465-473。
[35] may k, song d d, wang ZFメトロ・カードとデビッドal.Effect ofultrahigh圧力 治療 on volatile compounds in ニンニク[J]。誌 食品 過程 2011年工学、34(6):1915-1930。
[36] abe k, myoda t, nojima s 硫黄の heterocyclic compounds that 古にんにく抽出物の酸性臭に寄与する[j]。農業雑誌 食品 化学、2021年69(3):1020-1026。
〔37〕K NAJMAN ~ 0.010 K SADOWSKA A.The physicochemical特性、揮発性 compounds andtaste プロファイル of black ニンニク(Allium chinense sativum れる、ペースト and 粉 [J]。応用Sciences-Basel、2022年12(9):4215。
[38]マーティンスはN, PETROPOULOS S,カレカノ I.Chemical構成 and bioactive compounds of ニンニク(Allium chinense sativum真)と 影響 by 平滑化 and post-harvest 条件: 審査か[J]。2016年食品化学は、211:41-50。
[39] BEDRNICEK J、LAKNEROVAI LORENC F et al.The use of 熱を process to produce black ニンニク:違い in physicochemicalと sensory 特性を 7品目の fresh 大蒜か[J] .Foods、2021年まで、あと10 (11):2703
[40]元 H、孫 L J、陳 M, et al.The 比較 of 内容 of 砂糖・Amadori Heyns compounds in fresh と黒 ニンニク[J]。誌 of 食品 2016年科学81(7):1662-1668。
[41] RIOS-RIOS K L, MONTILLA A OLANO Aメトロ・カードとデビッド。Physicochemical changes and ぬいぐるみ 文化財 during black garlic 详しい陈述: 審査 [J]。動向 in 食品 科学 & 技術を取り入れた88:459-467 2019年です。
[42] najman k, sadowska a, hallmann e .熱処理の影響 生物活性、抗酸化物質、物理化学についてです 従来の属性 有機農業 black ニンニク(Allium chinense sativum l)か[J]。応用科学-バーゼル10(23)、2020部8638で検出する。
[43]劉 CF、LULD、YANGCJなど al.Effects of 熱 治療 「オールイン」に and its 関連 知りませ during black garlic 処理か[J]。LWT-Food 科学 and 技術、2022年159:113158。
[44]あり得るな丘陵地を捜そ M、アルアメド W.Black ニンニク: 審査 of its 生物意味 [J]。journal of food biochemistry,2022,46(12):e14394。
[45] SASMAZ H K、SEVINDIK O、アダルEなど al.Comparative評価 of quality パラメータ and bioactive compounds 白い と黒ニンニクか[J]。european food research and technology,2022,248(9):2393-2407。
[46]ちゃん K , H、CHANGCK GAVAHIAN M, et al.The impact 異なる 前処理 プロセス(凍結,超音波と高圧)感覚に and 機能 文化財 黒 ニンニク(Allium chinense sativum L)か[J] .Molecules 2022(27)(20): 6992。
[47] CHENY T、辰弥さん、李 証拠は無いetal ?の 戦略 for 加齢ニンニクにおけるy‐グルタミルトランスフェラーゼ活性とs-アリル- (l)-システインの酵素合成を促進する high 水圧 圧力pretreatments [J]。食品 化学、316:126347、2020。
[48] RIOS-RIOS Kさん L, GAYTAN-MARTINEZ M、リベラ- PASTRANADMなど al.Ohmic 暖房 前処理 加速黒 garlic 処理か[J]。LWT-Food 科学 and 技術、2021年151:112218。
[49] LIUCF LULD、YANGCJなど al.Effects of thermal treatment alliin日 and its 関連 sulfides during black garlic 処理か[J]。LWT-Food 科学 and 技術、2022年159:113158。
[50] wu p, liu p x, wangy t,et 特性成分のパターンの変更 in black garlic during 処理分析 by 超 性能 液体 chromatography-triple四極 し 大量 離イオン化[J]。食品 科学、2024年、45(1):82-90。
[51] zhang z s, lei m m, liu r,et al 「オールイン」が 内容 and 抗酸化 活動 of black ニンニク中 热加工ができか[J]ます誌 食品 2015年生化学、39(1):39-47。
ペ[52] SE、CHOSYウォン Y D et al.Changes in S-allyl て内容 and physicochemical 文化財 of black garlic 排出される 治療か[J]だ。LWT-Food 科学 and 2014年技術、55(1):397-402。
[53] afzaal m, saeed f, rasheed r,et al 治療 文化財 of black ニンニク: 批判審査か[J]。国際学術誌「食品 器物や2021年24(1):1387-1402。
[54]丁 YFさん、ZHOUXF、仲代达矢 Y et al.Metabolite、揮発性 と抗酸化の概要 of black garlic 記憶され in 異なる 包装材料か[J]食品 制御、2021年127:108131。
[55] wang cc, zheng z j, luxm,et al and 安全性評価 of5-hydroxymethylfurfural in black ニンニク[J]。食べ物や科学2022年、43(3):100-105。
[56] LUXM LINY、QIAOXGメトロ・カードとデビッドal.Composition分析 と抗酸化 properties of black garlic 抽出[J]。誌 of 食品 and 麻薬 2017年分析、25(2):340-349。
[57] lu x, li n, qiao x,et al.Effects 多糖類を熱処理する方法です degradation during black garlic 処理か[J]。LWT-Food 科学 and 技術を取り入れた95:223-229、2018年です。
[58] UTAMA gl, rahmi z, sarim p,et al と多糖類 compounds of black ニンニク(Alliumsativum l)か[J]。現在 ^『食の科学』2017年8月号、17 - 17頁。
[59] SUHARTIARLSWS。細菌に対する総酸度分析と endophytic 菌類 プロファイル during black garlicprocessing ニンニク(allium sativum l .)からと shallot(allium ascalonicum l .) [j]。^『仙台市史』通史編2(通史編3)188-194頁。


 英語
英語 フランス
フランス スペイン
スペイン ロシア
ロシア 韓国
韓国 日本
日本



