Natural Hop Extracts Empower Innovation in Bone Health Products
As the global population ages and health awareness rises, bone health concerns have transcended traditional age groups to become a core health issue across all demographics。 Market demand for safe, effective, and natural bone nutrition solutions has reached unprecedented levels, driving the industry to continually seek innovative ingredients。
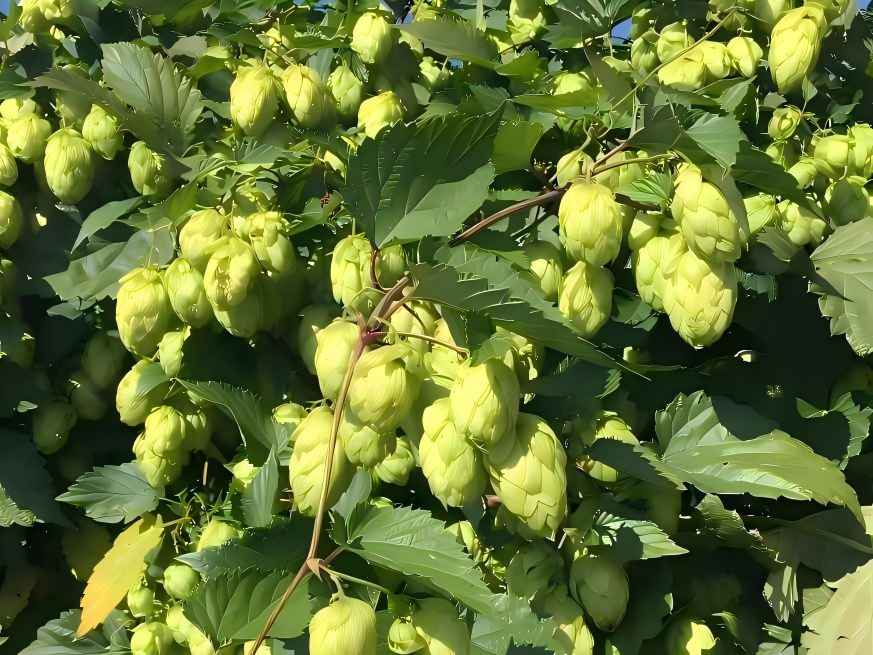
Against this backdrop, an innovative extract derived from natural ホップ (Humulus lupulus L。) is emerging with remarkable “bone-strengthening” potential。 Compared to common traditional ingredients like calcium supplements and vitamin D, hop extract (key active components: xanthohumol and flavonoids) offers a more fundamental and multifaceted mechanism of action.
Rather than merely supplementing bone-building materials, it gently regulates bone metabolism balance through its unique estrogen-like effects. Simultaneously, its potent antioxidant activity mitigates oxidative stress-induced bone cell damage. This dual-pathway approach effectively maintains bone homeostasis by simultaneously “increasing supply” and “reducing expenditure,” offering a revolutionary scientific perspective for product development.
As a premium natural ingredient supplier, グリーン春 Technology deeply focuses on this cutting-edge field, committed to providing customers with high-purity, high-potency standardized hop extract ingredients.

Why choose our ingredients:
⭐ Scientific moat for product innovation: Backed by robust osteoporosis research data, empowering your products to build unique selling points and stand out in a homogenized market.
⭐ Market positioning as “natural, safe, and effective”: Satisfies modern consumers' dual pursuit of natural solutions and scientifically proven efficacy, significantly enhancing brand value and trust.
⭐ One-stop ingredient solutions: We control quality from the source, ensuring ingredient stability and reliability to provide solid support for your new product development and mass production.
Green Spring Technology invites industry partners to jointly unlock the modern health potential of this ancient plant. Harness the power of technology to create beauty through health, and together seize the next strategic high ground in the bone health market.
1 The Scientific Secrets of Hops' Core Components
Hops extract stands out due to its unique and rich bioactive compounds. Its core value primarily stems from the following key components:
1.1 Flavonoids (Core Functional Agents)
Flavonoid compounds, represented by xanthohumol, are the star ingredients in hop extracts with the greatest potential for promoting bone health. Xanthohumol, a natural isoprenoid flavonoid unique to hops, exhibits exceptional estrogen-like effects and potent antioxidant activity. These dual properties enable bidirectional regulation of bone metabolism—promoting bone formation while inhibiting resorption—effectively maintaining bone density and homeostasis. This makes it an ideal choice for developing natural functional ingredients against osteoporosis.
1.2 Resinous Components (Synergistic Partners)
Resinous components in hop extracts, particularly unique bitter acids (such as α-acids and β-acids), contribute significant biological activity. Research indicates these compounds synergize with flavonoids to further support anti-inflammatory and antioxidant pathways. Together, they create a healthy microenvironment for bone cells, indirectly promoting skeletal health.
1.3 Essential Oils and Other Components (Natural Quality Foundation)
Essential oils and other constituents ensure the raw material's natural purity. High-quality, standardized extraction processes maximize retention of core active ingredients (like xanthurenic acid) while guaranteeing batch-to-batch consistency and reliability. This establishes a solid foundation for the superior quality and consistent taste of the final bone health product.
In summary, hop extracts—particularly those rich in xanthopyrolidones—provide robust scientific support for their application in bone health. This makes them an innovative natural ingredient that addresses specific health needs while aligning with the “clean label” trend.
2 Insights into Innovation and R&D for Bone Health Products Powered by Natural Hop Extracts
Natural hop extracts are emerging as a key driver of innovation in bone health products. Osteoporosis, a systemic metabolic bone disorder characterized by reduced bone mass and impaired microarchitecture, has drawn increasing attention for its prevention and treatment. Recent scientific research has progressively revealed the multifaceted benefits of hops in maintaining skeletal health, providing robust support for their application in functional foods and health supplements.
Hops extract exerts anti-osteoporotic effects through multiple mechanisms. Firstly, its rich flavonoid components—such as 8-isopentenylnaringenin (8-PN) and quercetin—exhibit significant phytoestrogen-like activity. These compounds bind to human estrogen receptors, alleviating bone metabolic disorders caused by estrogen deficiency. Research indicates that kaempferol effectively suppresses abnormal expression of bone turnover markers, improves bone microarchitecture, and enhances bone density.
Second, hop extract exhibits outstanding antioxidant properties. Components like kaempferol synergistically enhance antioxidant effects and mitigate oxidative stress damage to osteoblasts by activating the Nrf2 pathway, thereby supporting bone health.
More importantly, hop extract helps regulate the balance between bone formation and resorption, preserving bone homeostasis. Experimental evidence demonstrates that active components like xanthohumol, humulone, and lupulone not only promote osteoblast proliferation, differentiation, and mineralization while increasing expression of bone formation-related proteins, but also inhibit osteoclast generation and activity. This reduces levels of bone resorption markers, effectively preventing bone loss.
Currently, hops are utilized globally in the development of various bone health products. Clinical observations also indicate that consuming beverages containing xanthohumol can alleviate oxidative damage in the human body and regulate bone metabolism indicators. These studies not only confirm the potential of hop extracts in preventing and treating osteoporosis but also provide reliable scientific support for their application in next-generation bone health products.
Hops, this traditional natural ingredient, is injecting new vitality into bone health product innovation through its multi-pathway, multi-target skeletal protective functions. It holds promising prospects for broader applications in the functional food and health supplement sectors.
3 Hops Extract: A Natural Force Driving Innovation and Development in Bone Health Functional Foods
Beyond traditional beer brewing, hop extract, as a distinctive natural ingredient, is gaining increasing attention for its dual medicinal and dietary value. It has been utilized globally in the development of various innovative bone health products.
A series of functional products featuring hops as a core ingredient has emerged on the market, such as hop pellets from Citra (USA) and Saaz (Czech Republic), hop capsules from Nature's Way (Australia), and hop concentrate tablets from Menomax (Finland). These products, backed by modern research, demonstrate promising potential in combating osteoporosis.
Studies indicate that specific standardized hop extracts exhibit significant efficacy in preventing and treating osteoporosis. For instance, in an ovariectomized rat model, hop extracts not only ameliorated estrogen-deficiency-induced weight gain, lipid metabolism abnormalities, and hot flashes but also markedly increased femoral bone density and improved bone microarchitecture. More significantly, comparative experiments confirm that the bone-protective active components in beer primarily originate from hops, rather than alcohol or other brewing ingredients.
Human clinical observations further support its application potential. Studies found that after 14 consecutive days of consuming beverages containing xanthurenic acid, subjects exhibited significantly reduced oxidative damage markers and improved bone metabolism-related biomarkers. This indicates hop extracts can effectively support bone health by alleviating oxidative stress and regulating bone metabolism.
This scientific evidence provides a solid foundation for innovating bone health products centered on hop extract, clarifying its development value and application prospects in functional foods and health supplements.
4 Technology-Empowered: Hop Extract Raw Materials for High-Quality Bone Health Products
As modern pharmacology continues to uncover the multifaceted mechanisms of hops in combating osteoporosis—such as promoting bone formation, inhibiting bone resorption, and alleviating oxidative stress—the application prospects of hop extracts as functional food ingredients are increasingly clear. While current research focuses on postmenopausal osteoporosis models, exploration into additional application scenarios, such as senile osteoporosis, is gradually underway.
Against this backdrop, Green Spring Technology leverages local resources and independent R&D strengths to provide high-purity, standardized hop extracts and xanthohumol raw materials with consistent efficacy.
Core advantages:
· Traceable and Controllable Raw Materials: Selecting hops from high-latitude regions like Xinjiang, establishing end-to-end quality management from cultivation to harvest;
· Advanced and Efficient Processes: Utilizing green extraction and precision separation technologies to ensure high yield and stability of active components like xanthone;
· Defined Composition and Clear Standards: Implementing a rigorous quality indicator system to guarantee batch-to-batch consistency, providing a reliable raw material foundation for customer product innovation.
Green Spring Technology empowers traditional resources through innovation, continuously advancing the application of hop extracts in functional foods for bone health and other sectors. We deliver natural solutions that blend Chinese characteristics with international standards.
Contact us for samples or detailed product specifications at helen@greenspringbio.com or WhatsApp: +86 13649243917.
参照
【1】柳玉美、唐建、柳奎彦。ホップの化学的研究とビール醸造との関係[j]。^「science and technology」。brewing science and technology .(2006年). pp . 71-75. 2013年3月27日閲覧。
[2] liu jingxue, jiang yu, xie hehui, et al。漢方薬ホップの薬理作用に関する研究[j]。2019年日刊製薬練習37(1):詳細に説明。
[3] lin liuyue, jiang yiping, zhang qiaoyan, et al。ホップの化学成分と薬理活性に関する研究[j]。^「chinese journal of traditional and western medicine, 2017, 42(10): 1830-1836」。chinese journal of traditional and western medicine(2017) . 2018年3月30日閲覧。
[4]劉板野友美(20)。ホップの化学成分と薬理作用に関する研究[j]。2009年食物科学専攻、30(23):521-527。
[5] liu yumei, gu xiaohong, tang jian, et al。貯蔵条件がホップの化学組成に与える影響[j]。2006年(平成18年):487-490。
[6] li jun, cui chengbin, cai bing, et al。ホップにおけるフラボノイドの研究[j]。^『仙台市史』通史編、通史館、2008年(平成20年)、107 - 107頁。
[7] power f b, tutin f, rogerson h . cxxxv:ホップの成分[j]。^ a b c d e『人事興信録』第1版、大正13年、123 - 123頁。
[8] KOVAČEVIČM KAČM Solid-phase microextractionのホップて行いますか[J]。^ a b c d e f g h i j chromatogr a, 2001, 918(1): 159-167。
[9] liu yumei, wang liping, bai shanshan, et al。研究が揮発成分についてのαマルコポールホテル-acidか[J]飛び乗って新疆ウイグル大学学術誌(自然科学版),2015(4):392-398,409。
-
Prev
Exploring Hop Extract as a Clean-Label Ingredient Solution for Natural Preservation
-
次
Natural Xanthohumol in Hops Extract Enhances Bone Health Product Upgrades


 英語
英語 フランス
フランス スペイン
スペイン ロシア
ロシア 韓国
韓国 日本
日本




