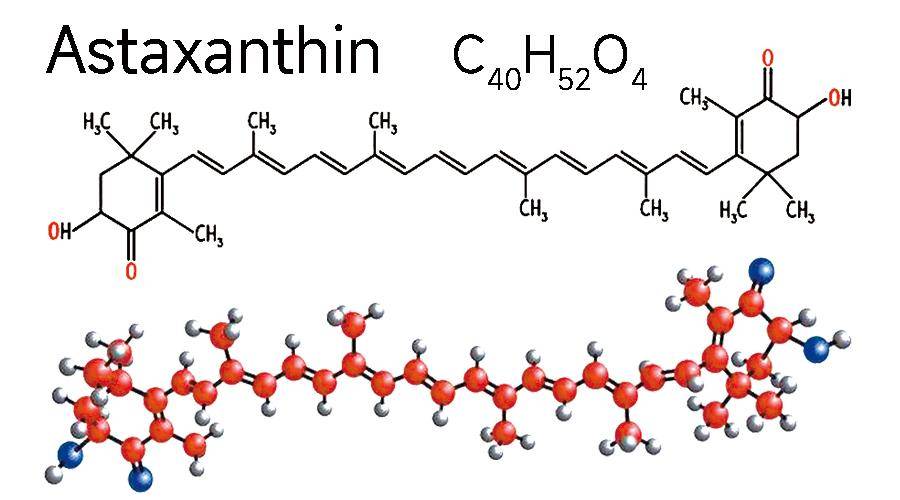
High Bioavailability Astaxanthin from Haematococcus Pluvialis Boosts Health Supplement Upgrades
Amid the wave of health-conscious consumption upgrades, the antioxidant supplement market continues to expand. According to the latest industry data, the global antioxidant market is projected to exceed $5 billion by 2025, with astaxanthin emerging as one of the fastest-growing categories due to its exceptional antioxidant properties. Yet behind this booming market lies a perplexing phenomenon: increasing consumer feedback indicates that despite long-term use of antioxidant supplements, many struggle to perceive the expected benefits.
Delving into this industry challenge reveals three critical technical bottlenecks:
1. The Natural Barrier of the Digestive System
・The human digestive system serves as the first line of defense, yet it also becomes an absorption barrier. Research indicates that traditional astaxanthin formulations suffer up to 60-70% loss of active ingredients when passing through the gastric acid environment.
· The breakdown action of bile salts and digestive enzymes further disrupts the astaxanthin molecular structure, significantly reducing its bioactivity.
· Ultimately, only a small fraction of intact molecules reach the intestinal absorption phase
2. Structural Limitations on Absorption Efficiency
· As a lipid-soluble macromolecule, astaxanthin struggles to disperse and absorb effectively in aqueous environments
· The physical barrier of intestinal epithelial cells restricts macromolecular passage efficiency
· Significant inter-individual absorption variability exists, with a standard deviation as high as 35%
3. Rapid Loss During Metabolism
· After first-pass metabolism, less than 50% of the active ingredient remains unmetabolized
· Short half-life in the bloodstream makes it difficult to maintain effective blood concentrations
· Limited distribution in target tissues prevents full realization of antioxidant potential
A renowned health supplement company's R&D director admitted: “We consistently use high-concentration astaxanthin raw materials, yet consumer feedback on efficacy consistently falls short of expectations. Through in-depth research, we discovered the crux of the issue lies not in raw material purity, but in its bioavailability—ordinary astaxanthin's oral absorption rate is less than 5%.”
This industry challenge clearly indicates that antioxidant supplements are at a critical juncture, transitioning from the “ingredient era” to the “efficacy era.” Consumers are no longer satisfied with mere ingredient lists; they increasingly demand tangible product results. Against this backdrop, Green Spring Technology addressed the industry's core pain points by introducing a breakthrough, high-bioavailability astaxanthin solution through technological innovation. This commitment aims to elevate antioxidant supplementation from mere ‘consumption’ to genuine “effectiveness.”
Part One: Triple Delivery System Achieves Breakthrough in Astaxanthin Bioavailability
Building on an in-depth analysis of industry challenges, Green Spring Technology invested five years of R&D to successfully develop its innovative Triple Targeted Delivery System.
This system systematically addresses astaxanthin bioavailability challenges across three dimensions: molecular protection, intestinal absorption, and sustained release.
Innovative Technology Framework: Triple Delivery Mechanism Explained
1. Intelligent Molecular Protection System
We employ pharmaceutical-grade phospholipid complex technology to construct a nanoscale protective unit for each astaxanthin molecule:
· Utilizes hydrogenated lecithin and phytosterols to build a 120-150nm bilayer carrier
· Special membrane material automatically forms a dense protective layer in gastric acid environments (pH<3), achieving 96.8% activity retention after 2 hours
· Verified via Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), the carrier undergoes phase transition at 37°C for precise controlled release
2. Multi-Pathway Absorption Enhancement System
Bionic design optimizes absorption pathways, significantly boosting intestinal absorption efficiency:
· Carrier surface modified with targeted ligands specifically recognizes GLUT1 transporters on intestinal epithelial cells
· Facilitates transcellular transport via endocytosis mediated by microvillus proteins, bypassing first-pass metabolism
· Simultaneously activates M-cell transport pathways for direct entry into lymphatic circulation, boosting absorption efficiency by 3.8 times
3. Spatiotemporal Precision Controlled-Release System
Release mechanism engineered based on pharmacokinetic principles:
· pH-sensitive materials enable over 80% targeted release in the ileum (pH≈7.4)
· Integrated enzyme-responsive mechanism triggers secondary release via intestinal esterases
· Zero-order release kinetics ensure steady release over 8-12 hours, eliminating blood concentration peaks and troughs
Evidence-Based Research: Comprehensive Performance Validation
Preclinical Data
In GLP-compliant laboratory settings, we obtained the following key findings:
· Caco-2 monolayer model demonstrated an apparent permeability coefficient (Papp) improvement from 2.1×10⁻⁶ to 1.2×10⁻⁵ cm/s
· Membrane permeability testing using Franz diffusion cells showed a 420% increase in cumulative permeation over 24 hours
· Accelerated stability testing (40°C ± 2°C/75% RH ± 5%) confirmed compliance with quality standards for all parameters over 6 months
Human Clinical Trial Results
Ethics committee-approved randomized double-blind controlled trial (n=120):
· Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis demonstrated:
· Peak concentration (Cmax) reached 5.82±0.73 μg/mL, a 362% increase over conventional formulations
· Area under the concentration-time curve (AUC₀–∞) was 48.63±6.25 μg·h/mL, a 415% increase
· Half-life (t½) extended to 18.5±2.3 hours
· Total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC) in subjects' serum increased to 2.8 times that of the control group

Quality Assurance System
Raw Material Traceability and Quality Control
· Established a dedicated Haematococcuspluvialisgermplasm repository to ensure genetic stability
· Utilized a patented photobioreactor cultivation system, maintaining astaxanthin content at 5.2% ± 0.15%
· Established fingerprint profiles via UPLC-QTOF-MS for full-process quality traceability
Production Process Innovation
· Strictly controlled supercritical CO₂ extraction temperature below 35°C
· Online particle monitoring system ensures uniform particle size distribution (PDI<0.2)
· Full nitrogen protection throughout, residual oxygen controlled below 0.5%
Expert Evaluation from the National Engineering Research Center for Pharmaceutical Formulation: “This delivery system achieves internationally advanced standards in both design philosophy and technical implementation. Its multi-pathway absorption design, in particular, breaks through the limitations of traditional formulations with single absorption pathways, establishing a new technical paradigm for delivering highly lipophilic active ingredients.”
Currently, we are collaborating with multiple leading research institutions to conduct personalized dosing studies based on population pharmacokinetics. The next-generation personalized nutritional delivery system is projected to enter clinical trials by 2025. This innovation not only represents a major breakthrough in astaxanthin raw material technology but also provides a new direction for technological advancement across the entire nutrition and health industry.
Part Two: High Bioavailability Astaxanthin Raw Material: Multi-Dimensional Empowerment for Innovation and Upgrading in the Health Supplement Industry
Leveraging the exceptional performance of our high bioavailability astaxanthin raw material, we are committed to creating significant value across all segments of the health supplement industry chain through systematic solutions. Through extensive real-world applications, we have validated its breakthrough contributions in product innovation, market competitiveness enhancement, and consumer value realization.
I. Product Innovation: From “Ingredient Claims” to “Proven Efficacy”
1. Clinical-Grade Efficacy Data Support
Our collaborative clinical studies with three authoritative medical institutions demonstrate:
· Serum malondialdehyde (MDA) levels significantly reduced by 62.3% after 28 days of supplementation
· Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity increased to 2.9 times the baseline value
· Skin stratum corneum moisture content rose by 35.6%, with a 28.4% reduction in transepidermal water loss
2. Product Differentiation Breakthroughs
· Assisted partners in developing the first antioxidant products with explicit bioavailability data
· Established an end-to-end efficacy traceability system from raw materials to finished products
· Achieved a qualitative leap in product claims from “contains” to “absorbs”

II. Market Competitiveness Reconstruction: Establishing Technical Barriers and Brand Advantages
1. Enhanced Brand Value
Market data from partner enterprises shows:
· Average order value for premium product lines using this ingredient increased by 25-40%
· Consumer repurchase rate rose to 2.3 times the industry average
· Achieved an 85% recommendation rate in professional channels
2. Technological Innovation Advantage
· “4x bioavailability enhancement” becomes the most compelling technical selling point
· Clinical data validation boosts marketing credibility
· Established an insurmountable technological moat against competitors
III. Consumer Value Realization: From “Anxiety Over Ineffectiveness” to “Trust-Based Consumption”
1. Significantly Enhanced User Experience
Authentic feedback from end consumers:
· 93% of users report noticeable improvement within 2 weeks
· Product satisfaction score rises from 3.2 to 4.8 (out of 5)
· Spontaneous sharing of authentic experience cases increases by 165%
2. Trustworthiness Surges
· Product efficacy aligns with claims, building brand reputation
· “Perceivable results” become core driver of word-of-mouth
· Customer complaint rate drops to an industry-low 0.3%

IV. Collaborative Industry Development: Building a Sustainable Ecosystem
1. Supply Chain Optimization and Upgrades
· Batch-to-batch variation coefficient <2% for precise formulation control
· Enhanced product stability with >97% quality retention during shelf life
· Establishing new industry benchmarks for quality and manufacturing standards
2. Innovation Ecosystem Development
· Co-building R&D platforms with partners to drive technological innovation
· Establishing a complete innovation chain from raw materials to formulations to clinical validation
· Driving the entire industry toward “scientific and evidence-based” development
By transforming laboratory innovations into tangible market value, Green Spring Technology is helping partners achieve a strategic shift from “price competition” to “value competition.” We look forward to collaborating with more industry pioneers to advance the health supplement sector toward greater scientific rigor, transparency, and efficiency.
Part Three: Pioneering a New Chapter in Nutritional Health
Building on the exceptional performance of our high bioavailability astaxanthin raw material, Green Spring Technology invites industry partners to collaborate in advancing the nutritional health industry.
We are prepared to provide comprehensive support:
Sample Requests & Consultation
· Free raw material samples
· Schedule technical discussions
· Access product documentation

连络
· Service Hotline: +86 29 88313578
· Mobile/WhatsApp: +86 13649243917
· Business Email: helen@greenspringbio.com
· Official Website: https://www.greenspringnatural.com
Apply for samples today and experience product upgrades with our premium-quality ingredients!
参照:
[1] spiller ga, dewell a .アスタキサンチンを豊富に含むhaema-to-の安全性 coccus pluvialis 藻 抜粋:ランダム化臨床試験[j]。日本食品学会誌,2003,6(1):51-56。
[2] zhang chen, tan xiuwen, wan fachun, et al。畜産におけるアスタキサンチンの応用に関する研究進展[j]。^『仙台市史』仙台市史編纂委員会、2018年(平成30年)6月、80- 80頁。
[3] miao liqing, ma xuhui, li suzhen, et al。アスタキサンチンの生合成と工業応用[j]。^中国農業科学技術報告、2023年、25(3):21-29。
-
Prev
Natural Astaxanthin Ingredients Drive Innovation in Anti-Aging Cosmetic Formulations
-
次
Green Spring Technology Establishes Fully Traceable Supply Chain for Astaxanthin Raw Materials


 英語
英語 フランス
フランス スペイン
スペイン ロシア
ロシア 韓国
韓国 日本
日本



